Face Recognition: Deep Learning
DeepFace 1
Main idea
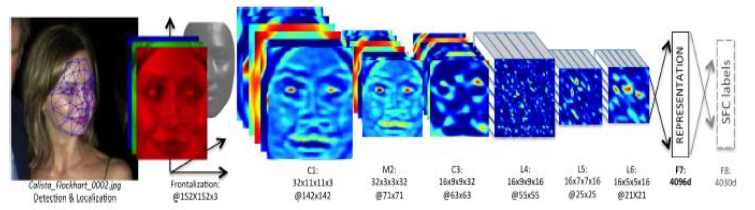
Learn a deep (7 layers) NN (20 million parameters) on 4 million identity labeled face images directly on RGB pixels.
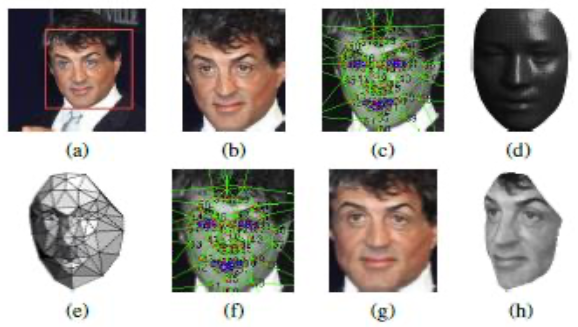
Alignment
Use 6 fiducial points for 2D warp
Then 67 points for 3D model
Frontalize the face for input to NN
Representation
Output is fed in $k$-way softmax, that generates probability distribution over class labels.
🎯 Goal of training: maximize the probability of the correct class
FaceNet2
💡Idea
- Map images to a compact Euclidean space, where distances correspond to face similarity
- Find $f(x)\ \in \mathbb{R}^d$ for image $x$, so that
- $d^2(f(x_1), f(x_2)) \rightarrow \text{small}$, if $x_1, x_2 \in \text{same identity}$
- $d^2(f(x_1), f(x_3)) \rightarrow \text{large}$, if $x_1, x_2 \in \text{different identities}$
System architecture
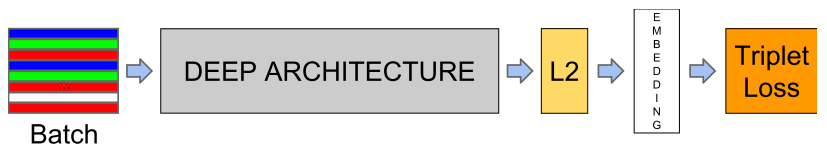
- CNN: optimized embedding
- Triplet-based loss function: training
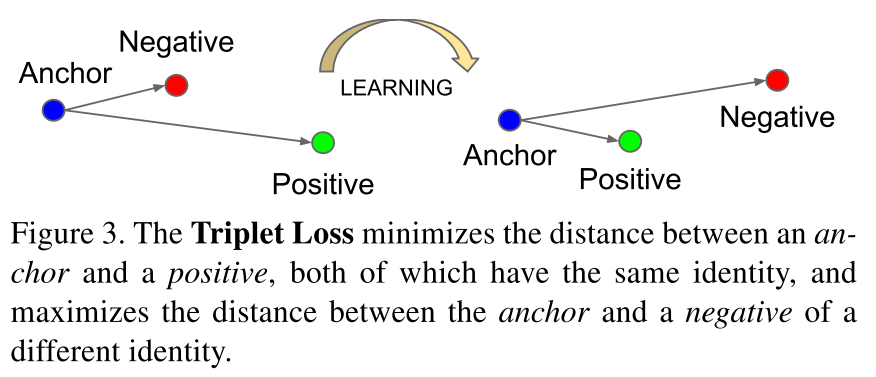
Triplet loss
Image triplets:
 $$
\begin{array}{c}
\left\\|f\left(x\_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x\_{i}^{p}\right)\right\\|\_{2}^{2}+\alpha<\left\\|f\left(x\_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x\_{i}^{n}\right)\right\\|_{2}^{2} \\\\
\forall\left(f\left(x\_{i}^{a}\right), f\left(x\_{i}^{p}\right), f\left(x\_{i}^{n}\right)\right) \in \mathcal{T}
\end{array}
$$
where
$$
\begin{array}{c}
\left\\|f\left(x\_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x\_{i}^{p}\right)\right\\|\_{2}^{2}+\alpha<\left\\|f\left(x\_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x\_{i}^{n}\right)\right\\|_{2}^{2} \\\\
\forall\left(f\left(x\_{i}^{a}\right), f\left(x\_{i}^{p}\right), f\left(x\_{i}^{n}\right)\right) \in \mathcal{T}
\end{array}
$$
where$x_i^a$: Anchor image
$x_i^p$: Positive image
$x_i^n$: Negative image
$\mathcal{T}$: Set of all possible triplets in the training set
$\alpha$: Margin between positive and negative pairs
Total Loss function to be minimized: $$ L=\sum_{i}^{N}\left[\left\|f\left(x_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x_{i}^{p}\right)\right\|_{2}^{2}-\left\|f\left(x_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x_{i}^{n}\right)\right\|_{2}^{2}+\alpha\right] $$
Triplet selection
Online Generation
Select only the semi-hard negatives and using all anchor-positive pairs of mini-batch
$\rightarrow$ Select $x_i^n$ such that $$ \left\|f\left(x_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x_{i}^{p}\right)\right\|_{2}^{2}<\left\|f\left(x_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x_{i}^{n}\right)\right\|_{2}^{2} $$
Results
- LFW: 99.63% $\pm$ 0.09
- Youtube Faces DB: 95.12% $\pm$ 0.39
Deep Face Recognition 3
Key Questions
Can large scale datasets be built with minimal human intervention? Yes!
Can we propose a convolutional neural network which can compete with that of internet giants like Google and Facebook? Yes!
Dataset Collection
Candidate list generation: Finding names of celebrities
- Tap the knowledge on the web
- 5000 identities
Manual verification of celebrities: Finding Popular Celebrities
Collect representative images for each celebrity
200 images/identity
Remove people with low representation on Google.
Remove overlap with public benchmarks
2622 celebrities for the final dataset
Rank image sets
- 2000 images per identity
- Searching by appending keyword “actor”
- Learning classifier using data obtained the previous step.
- Ranking 2000 images and selecting top 1000 images
- Approx. 2.6 Million images of 2622 celebrities
Near duplicate removal
- VLAD descriptor based near duplicate removal
Manual filtering
- Curating the dataset further using manual checks
Convolutional Neural Network
The “Very Deep” Architecture
3 x 3 Convolution Kernels (Very small)
Conv. Stride 1 px.
Relu non-linearity
No local contrast normalisation
3 Fully connected layers
Training
Random Gaussian Initialization
Stochastic Gradient Descent with back prop.
Batch Size: 256
Incremental FC layer training
Learning Task Specific Embedding
Learning embedding by minimizing triplet loss $$ \sum_{(a, p, n) \in T} \max \left\{0, \alpha-\left\|\mathbf{x}_{a}-\mathbf{x}_{n}\right\|_{2}^{2}+\left\|\mathbf{x}_{a}-\mathbf{x}_{p}\right\|_{2}^{2}\right\} $$
Learning a projection from 4096 to 1024 dimensions
On line triplet formation at the beginning of each iteration
Fine tuned on target datasets
Only the projection layers learnt
Y. Taigman, M. Yang, M. Ranzato and L. Wolf, “DeepFace: Closing the Gap to Human-Level Performance in Face Verification,” 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 2014, pp. 1701-1708, doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.220. ↩︎
Schroff, Florian & Kalenichenko, Dmitry & Philbin, James. (2015). FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. 815-823. 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298682. ↩︎
Omkar M. Parkhi, Andrea Vedaldi and Andrew Zisserman. Deep Face Recognition. In Xianghua Xie, Mark W. Jones, and Gary K. L. Tam, editors, Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), pages 41.1-41.12. BMVA Press, September 2015. ↩︎