Basic Input and Output
Source: RealPython
Reading Input From the Keyboard
input([<prompt>]): Reads a line from the keyboard. (Documentation)
pauses program execution to allow the user to type in a line of input from the keyboard
Once the user presses the Enter key, all characters typed are read and returned as a string
Note: the return string doesn’t include the newline generated when the user presses the Enter key.
Example
>>> user_input = input() foo bar baz >>> user_input 'foo bar baz'
If you include the optional
<prompt>argument, theninput()displays it as a prompt so that your user knows what to inputExample
>>> name = input("What is your name? ") What is your name? Winston Smith >>> name 'Winston Smith'
input()always returns a string. If you want a numeric type, convert the string with the appropriate built-in fuctions (int(),float(),complex())
Writing Output to the Console
You can display program data to the console in Python with print().
print() is capable of taking the following arguments:
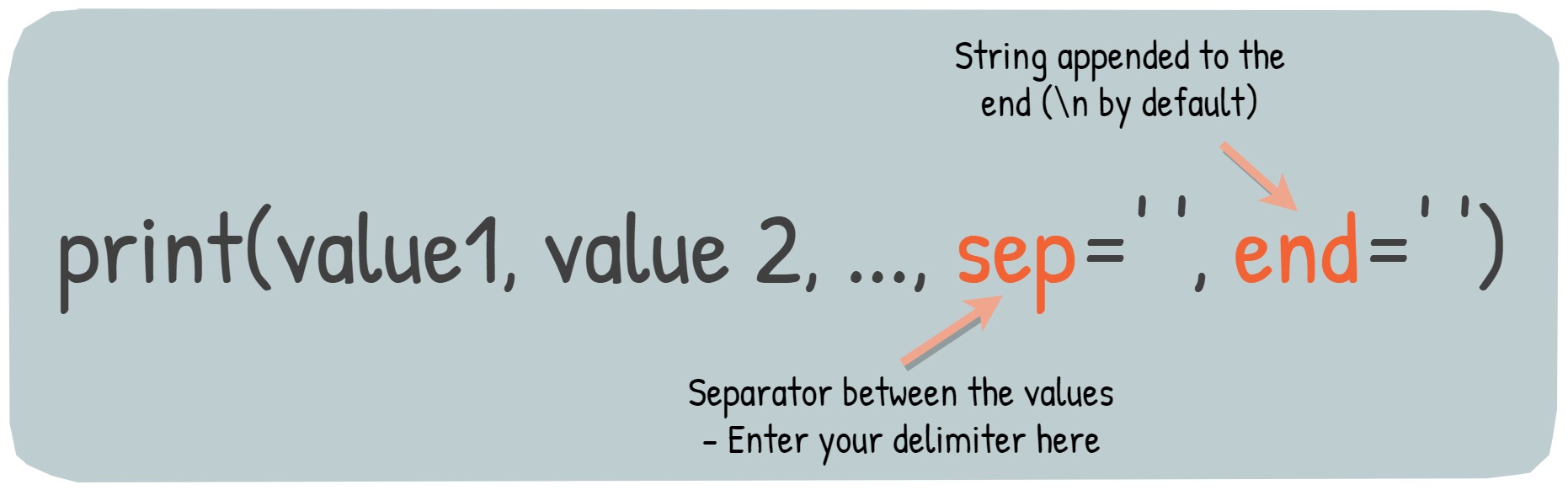
print() function
- The values (
value1,value2) mentioned above can be any string or any of the data types like list, float, string, etc. sep: Divides the values given as argumentsend: String appended to the end (\nby default)
Example
>>> arr = [1, 2, 3, 4 ,5]
>>> _ = [print("num", el, sep=": ", end="; ") for el in arr]
num: 1; num: 2; num: 3; num: 4; num: 5;
>>> d = {"foo": 1, "bar": 2, "baz": 3}
>>> for k, v in d.items():
... print(k, v, sep=" -> ")
...
foo -> 1
bar -> 2
baz -> 3