Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
Network Functions
Middleboxes and Network Functions
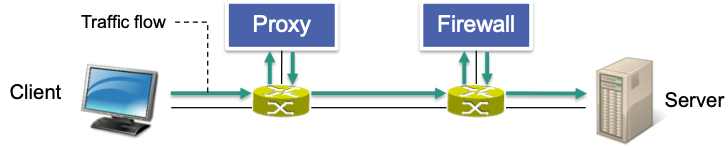
Middlebox
- Device on the data path between a source and destination end system
- Performs functions other than normal, standard functions of an IP route
Network function
- Functionality of a middlebox
- Executed on the data path
- E.g. Network address translation (NAT), firewall, proxy, load balancing, intrusion detection, …
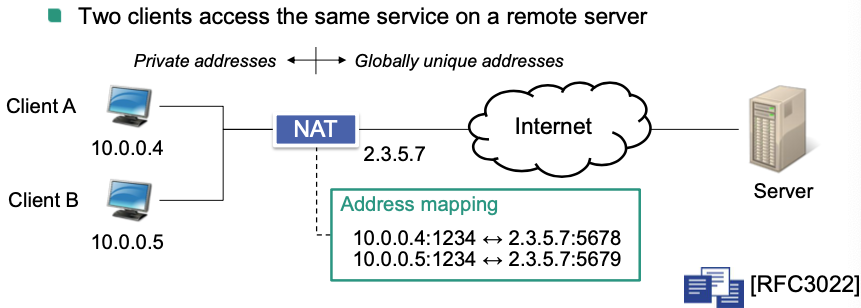
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Connects a realm with private addresses to an external realm with globally unique addresses
Problem: private addresses cannot be used for routing in the Internet
Solution: Exchange globally unique and private addresses when packets traverse network boundaries
$\rightarrow$ Clients in the private address range can share globally unique addresses
Example
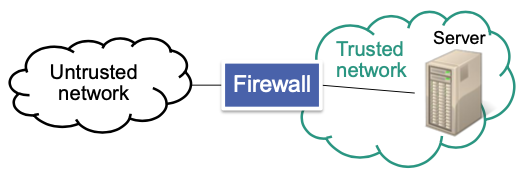
Firewall
Monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic
- Establishes barrier between trusted and untrusted networks
- Forwards or drops packets based on pre-defined rule set
Variants. e.g.
- Shallow vs. deep packet inspection
- Shallow: decisions are based on header fields only (e.g., IP and TCP protocol information)
- Deep: inspects content of higher layer protocols (e.g., detection of malware traffic in application layer protocols)
- Stateful vs. stateless processing
- Stateless: every packet is inspected independently of other packets
- Stateful: keeps state between packets (e.g., for every TCP connection to detect invalid sequence numbers)
- Shallow vs. deep packet inspection
Traditional Middlebox Deployment
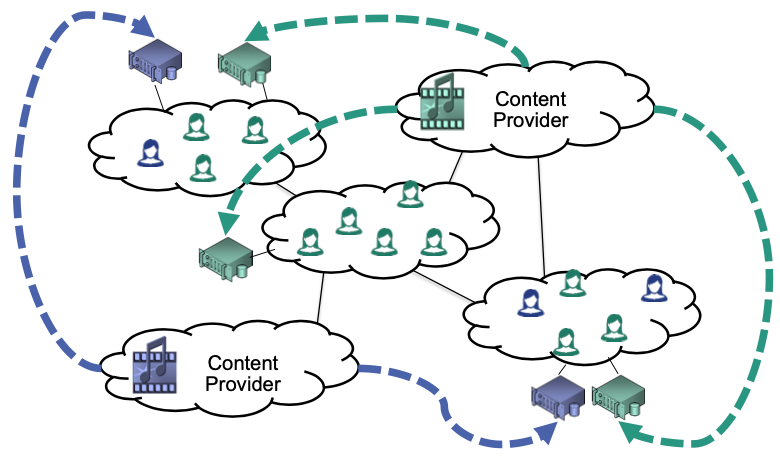
Example: Caching
Single content provider
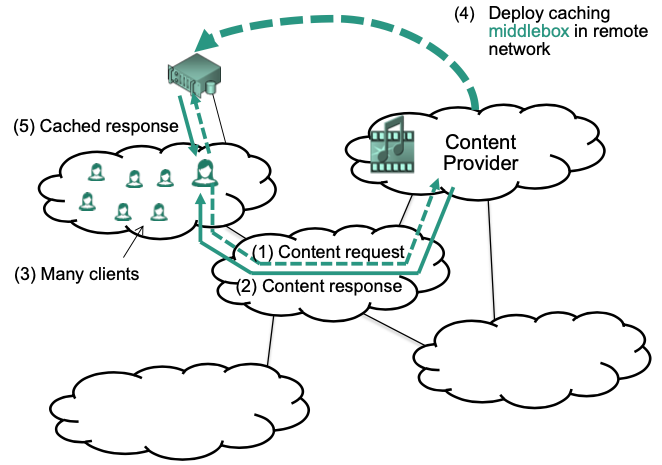
Multiple content providers
Place multiple middleboxes at different locations in the network
🔴 Problems
Middleboxes are often build as proprietary hardware
- Fast, but very inflexible
- Usually closed sourceblackbox for infrastructure operator
Static wiring
- Hard to setup / tear down
- Hard to move
- Hard to upgrade $\rightarrow$ introduce new or bigger boxes
Network operators have to manage many different vendor-specific boxes
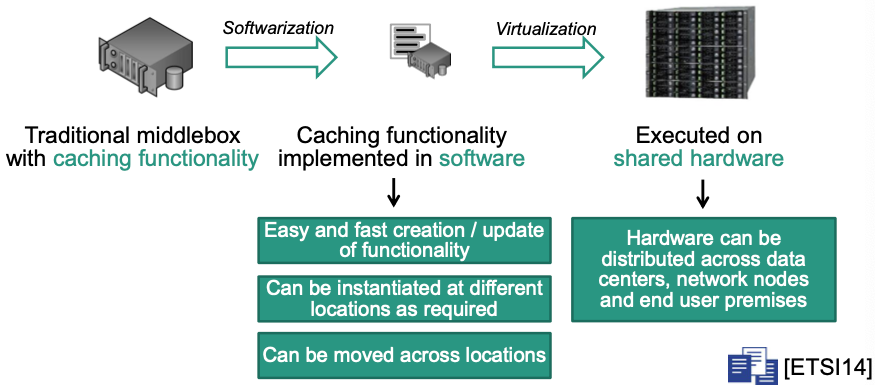
Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
💡Mimic ideas of cloud computing
- Implement network functions in software
- Use virtualization technology to decouple network functions from hardware
- Consolidate functionality on high volume servers, switches and storage
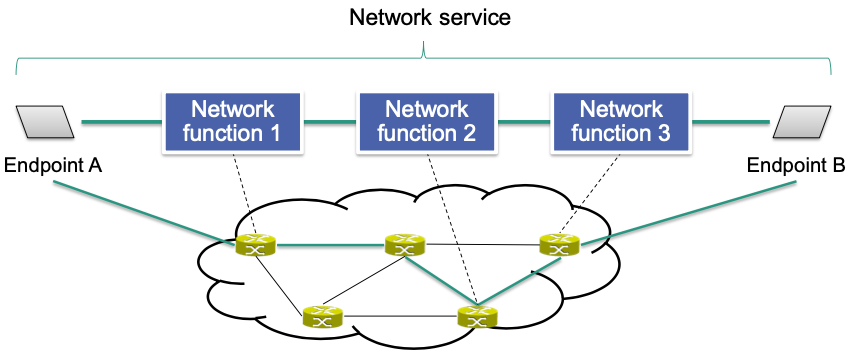
Network services combine multiple network functions
- End-to-end behavior of a network service is the combination of the individual network functions
👍 Benefits
- Resource sharing: Single platform for different applications and users
- Agility and flexibility: Services can scale to address changing demands
- Rapid deployment and innovation cycles: Providers can easily trial and evolve services
- Reduced costs
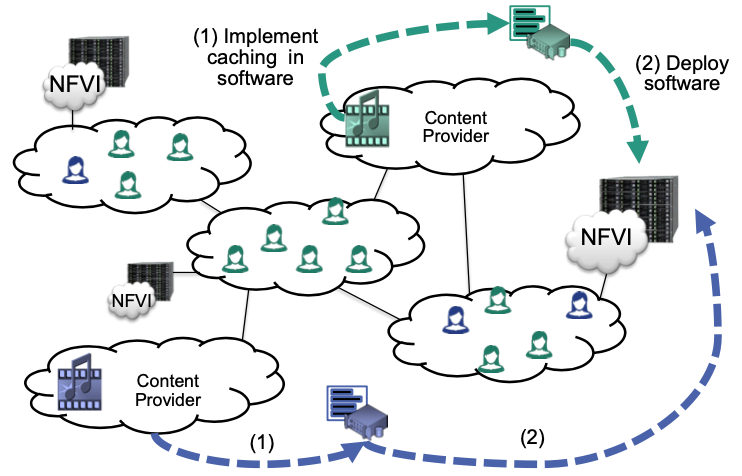
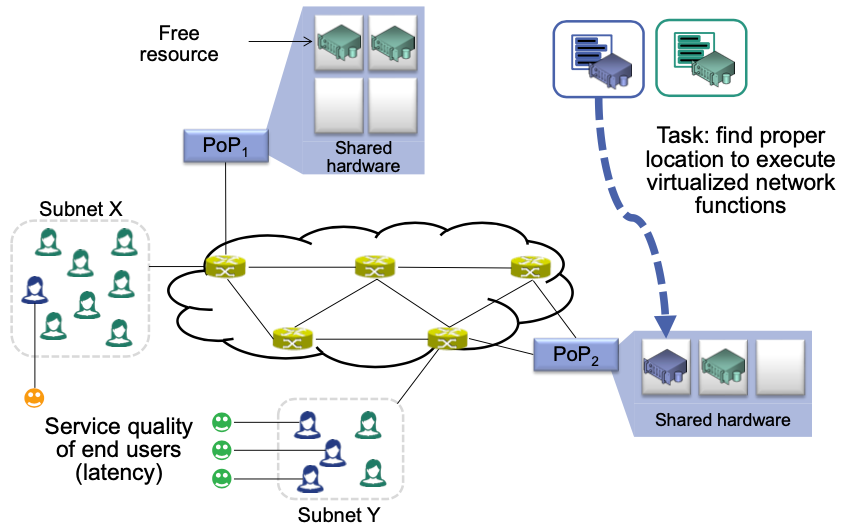
Consider the caching example above: Networks provide infrastructure for executing software-based network functions (NFV Infrastructure, NFVI)
Main Building Blocks of NFV
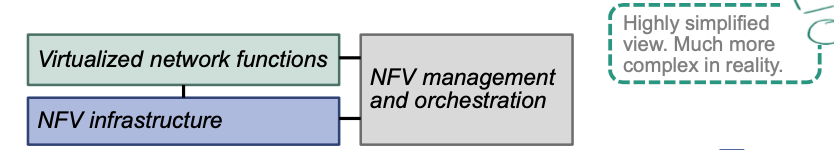
Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs)
- The actual network functions provided in software
- Independent of its deployment (e.g., hardware)
NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO)
- Lifecycle management of VNFs and network services
- Requests resources for VNFs
NFV Infrastructure (NFVI)
- Provides hardware, software and network resources for VNFs
- Decouples VNFs from underlying hardware
- Can contain multiple Points of Presence (PoP)
- Small data centers, located at different points in the infrastructure
- SDN is used to transparently reroute flows to PoPs
- Could also be done with MPLS or other technologies
- SDN and NFV complement each other very well
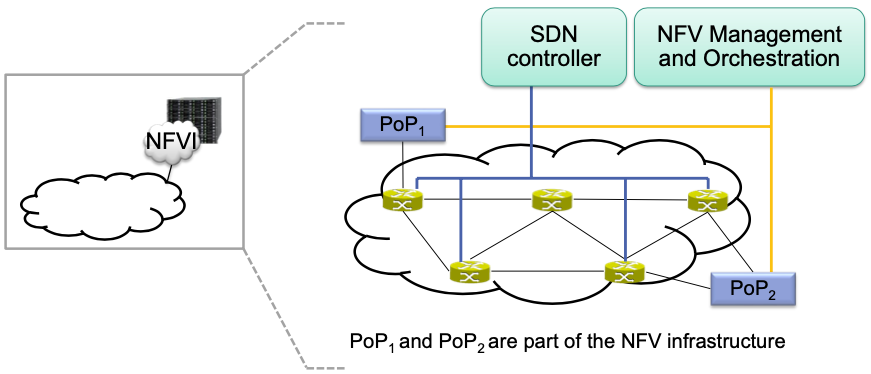
Simple deployment example
Virtualization
Provides a software abstraction layer between
- Hardware and
- Operating system and applications running in a virtual machine
$\rightarrow$ Offers a standardized platform for applications
The abstraction layer is referred to as hypervisor
- “Resource broker” between hardware and virtual machines
- Translates I/O from virtual machines to physical server devices
- Allows multiple operating systems to coexist on a single physical host
- Allows live migration of virtual machines to other hosts
Type 1 Hypervisor
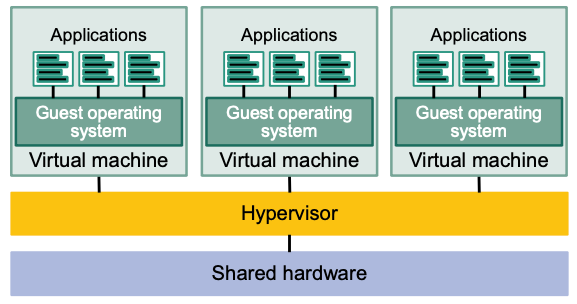
- Runs directly on hardware
- High performance
- Strong isolation between virtual machines
- Synchronizes the access of virtual machines to the hardware
Type 2 Hypervisor
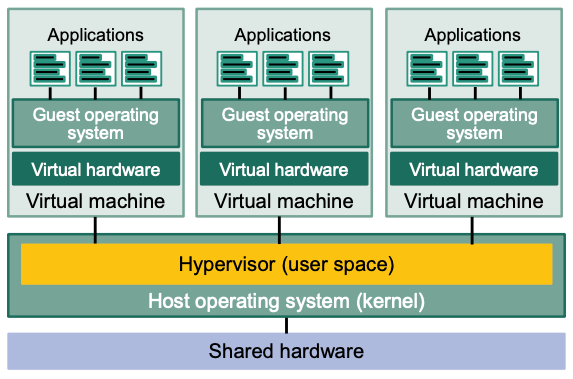
- Runs on top of a host operating system
- Hypervisor is executed as an application in user space
- Virtual machines provide virtual hardware to guest operating systems
- Interaction with virtual hardware is directed to physical devices through a virtual machine driver or the host operating system
Container-Based Virtualization
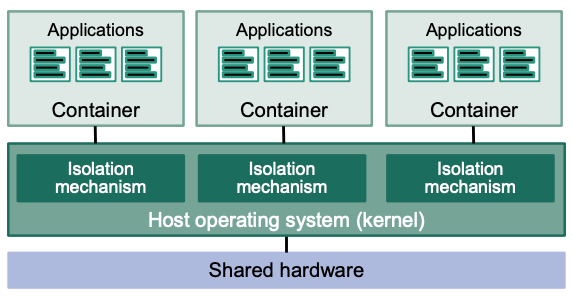
Single kernel provides multiple instances (containers) of same host operating system
No hypervisor involved
Isolation of containers is enforced by host operating system kernel
- Each container has its own view of the operating system
Applications in containers are executed by the host operating system
$\rightarrow$ Applications depend on host operating system
Kernel synchronizes access of containers to the hardware
Service Function Chaining (SFC)
- Ordered set of network functions
- Specifies ordering constraints that must be applied to flows
- Enables the creation of composite network services
- Transparent to end systems
- Examples
- Firewall $\rightarrow$ authentication server
- Load balancer $\rightarrow$ cache
- …
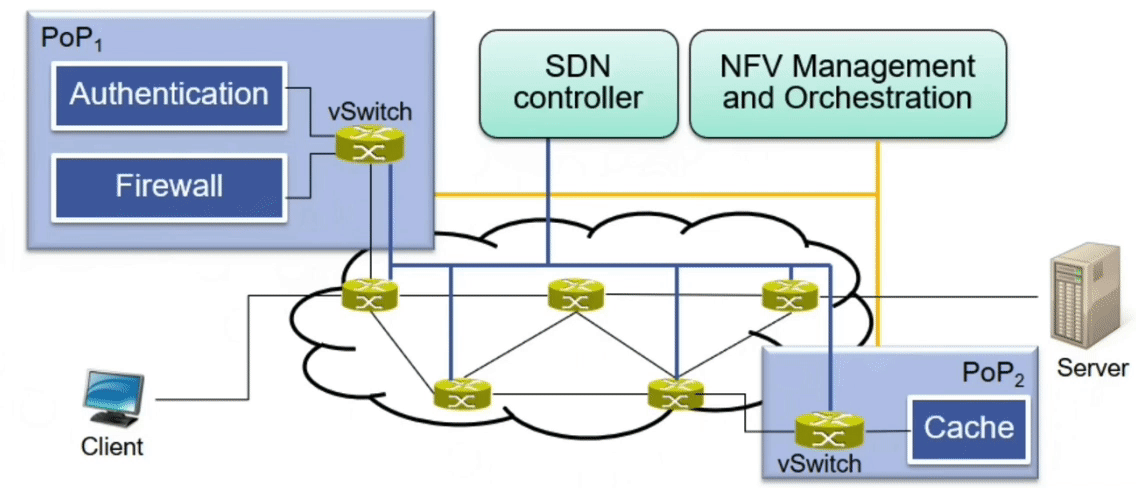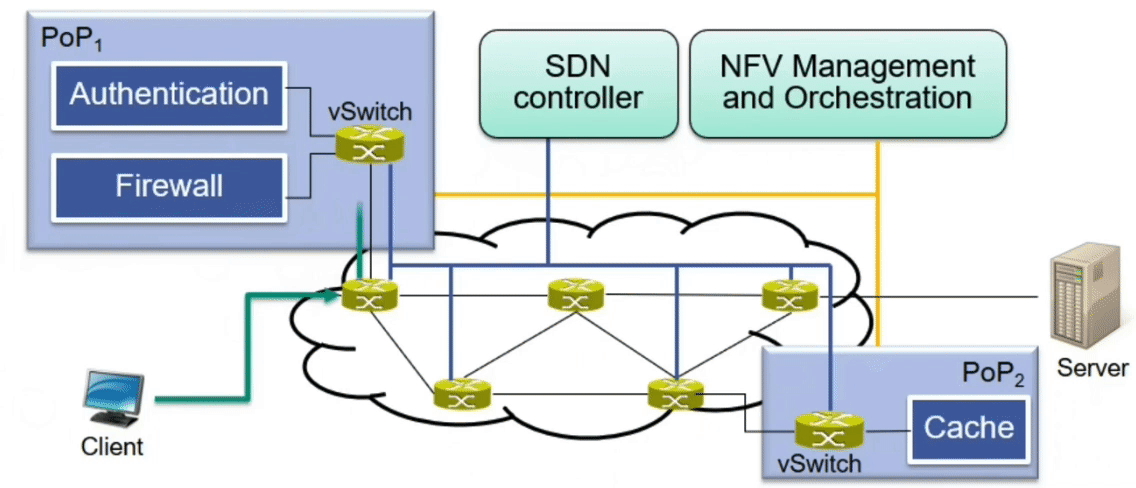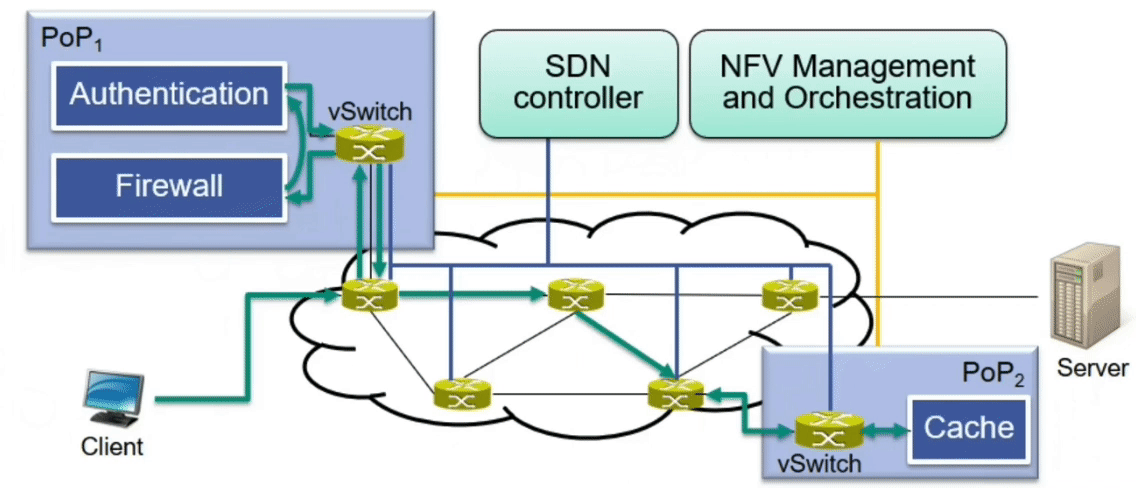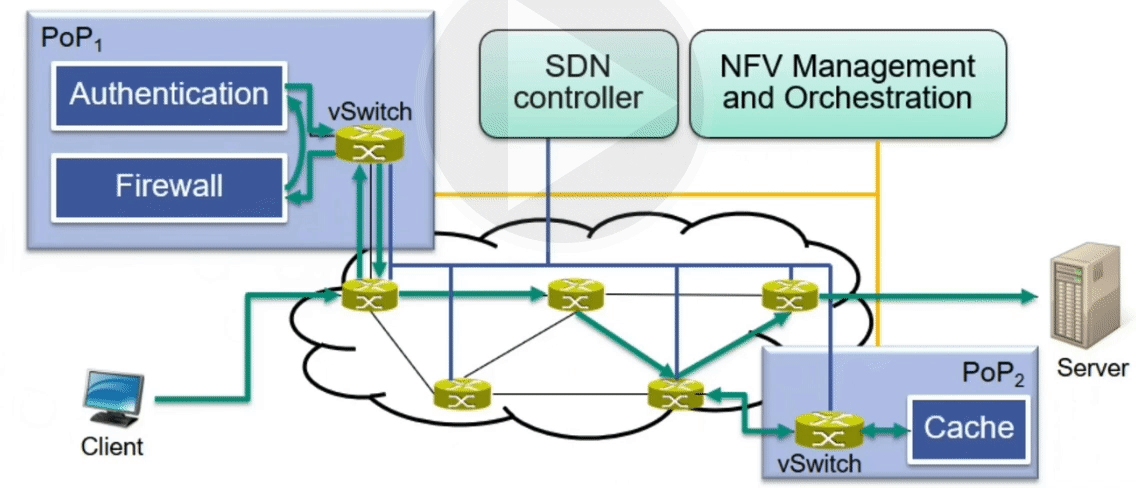
Example: Advanced Caching Scenario
Place additional firewall, authentication and cache on the data path
Sketch
Required VNFs are instantiated at appropriate PoPs
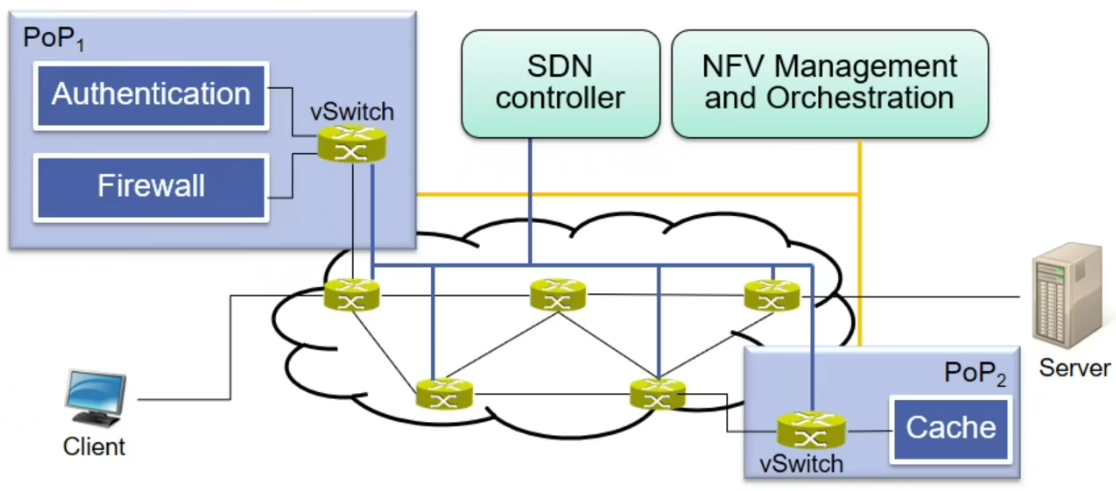
Service function chain is established (flow table entries in the data plane)
$\rightarrow$ Flow table entries enforce correct order of VNF traversal
MPLS-based Service Function Chaining
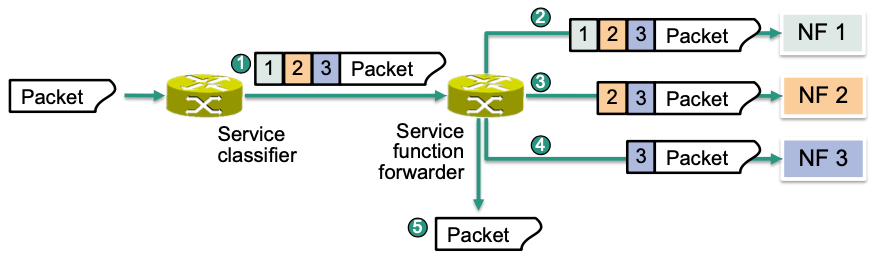
Service classifiers select appropriate service function chains (step 1)
- Select traffic to be processed in the chain
- Attach a stack of MPLS labels to packets to determine their path through the chain
Service function forwarders deliver packets to network functions
- The service function indicated by the topmost MPLS label is applied
- The topmost label is removed from the stack afterwards
(step 2 - 4)
- Normal traffic flow resumes when the MPLS stack is empty (step 5)
🔴 Challenges
- Security
- VNF performance
- VNF placement
- Reliability
- Testing and debugging
- Carrier grade requirements Existence with legacy networks
- …