Attention Mechanism
Human Attention
The visual attention mechanism is a signal processing mechanism in the brain that is unique to human vision. By quickly scanning the global image, human vision obtains a target area to focus on, which is generally referred to as the focus of attention, and then devotes more attentional resources to this area to obtain more detailed information about the target to be focused on and suppress other useless information.
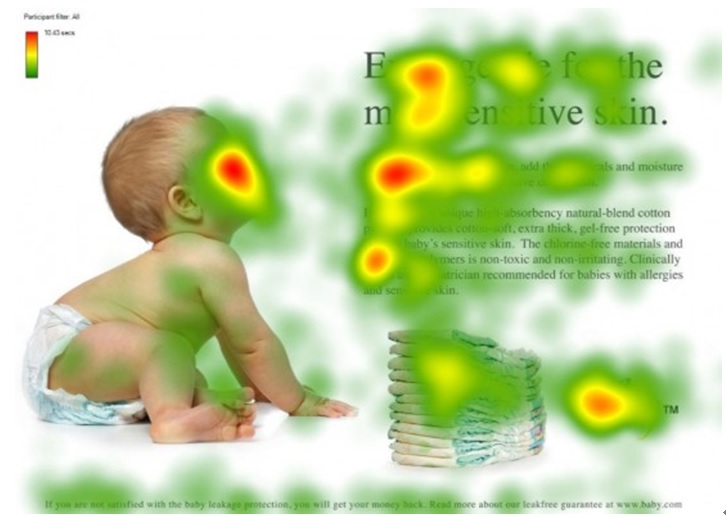
This figure demonstrates how humans efficiently allocate their limited attentional resources when presented with an image. Red areas indicate the targets to which the visual system is more attentive. It is clear that people devote more attention to the face, the title of the text, and the first sentence of the article.
Understanding Attention Mechanism
The attention mechanism in deep learning is essentially similar to the human selective visual attention mechanism. Its main goal is also to select the information that is more critical to the current task goal from a large amount of information.
The general process of attentional mechanism can be modelled as follows
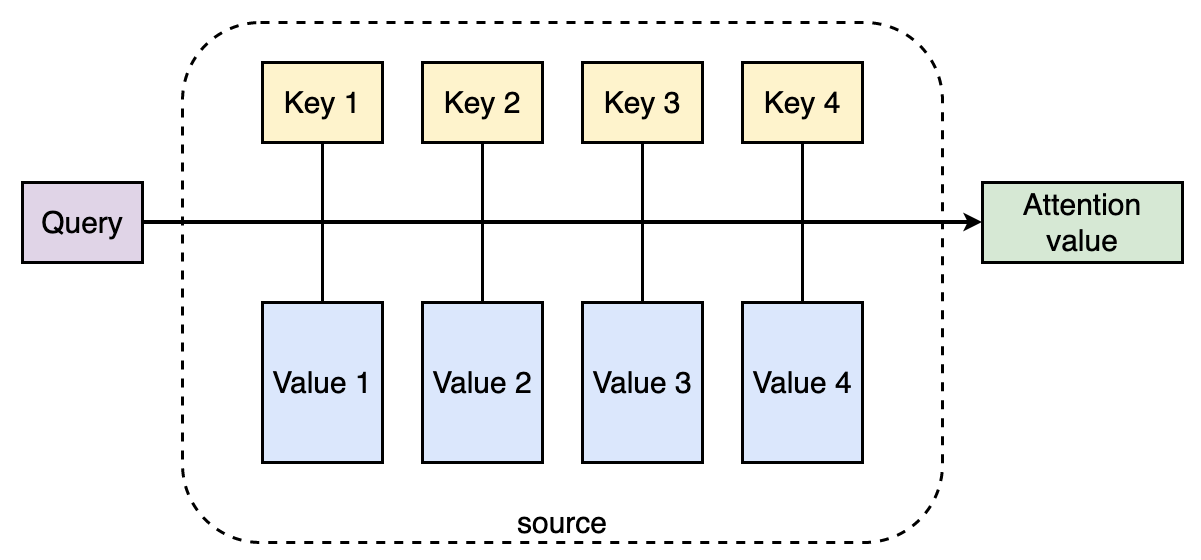
- In source, there’re a number of
<key, value>pairs. - Given a
queryof target, the weight coefficient of eachvalueis obtained by calculating the similarity/relevance between its correspondingkeyand thequery. - The
values are then weighted and summed up, which gives the final attention value.
So the attention mechanism can be formulated as: (assuming the length of Source is $N$)
$$ \operatorname{Attention}(\text{Query}, \text{Source}) = \sum\_{i=1}^{N} \operatorname{Similarity}(\text{Query}, \text{Key}\_i) \cdot \text{Value}\_i $$Understanding Attention Mechanism as “Soft Adressing”
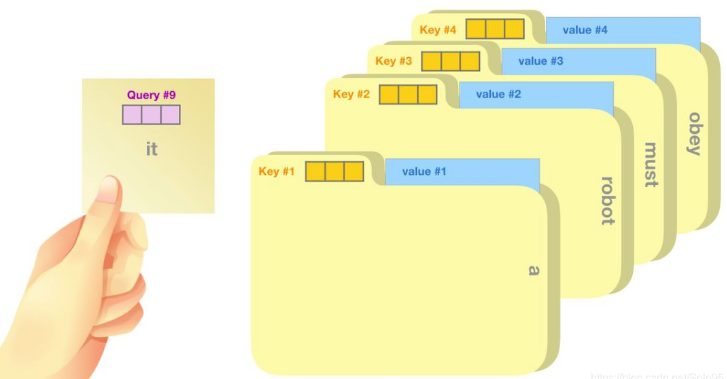
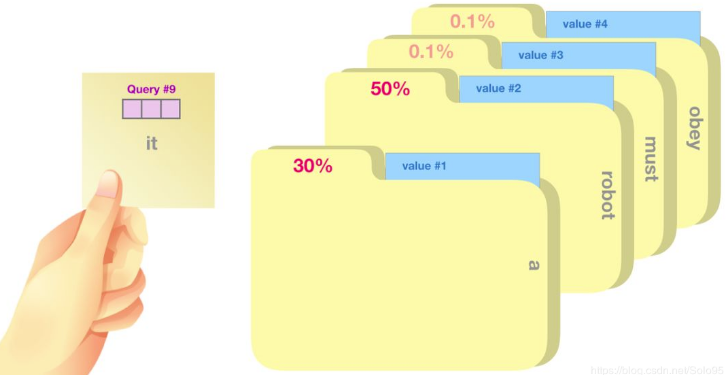
We can also understand attention mechanism as “soft adressing”
- A number of key(address)-value(content) pairs are stored in source(memory)
- Given a query, soft addressing is performed by comparing the similarity/relevance between query and keys.
- By general addressing, only ONE value can be found from the memory given a query.
- In soft addressing, values may be taken out from many addresses. The importance of each value is determined by the similarity/relevance between its address and the given query. The higher the relevance, the more important is the value.
- All retrieved values are then weighted and summed up to achieve the final value.
Example:
Computation of Attention
The computation of attention can be described as follows:
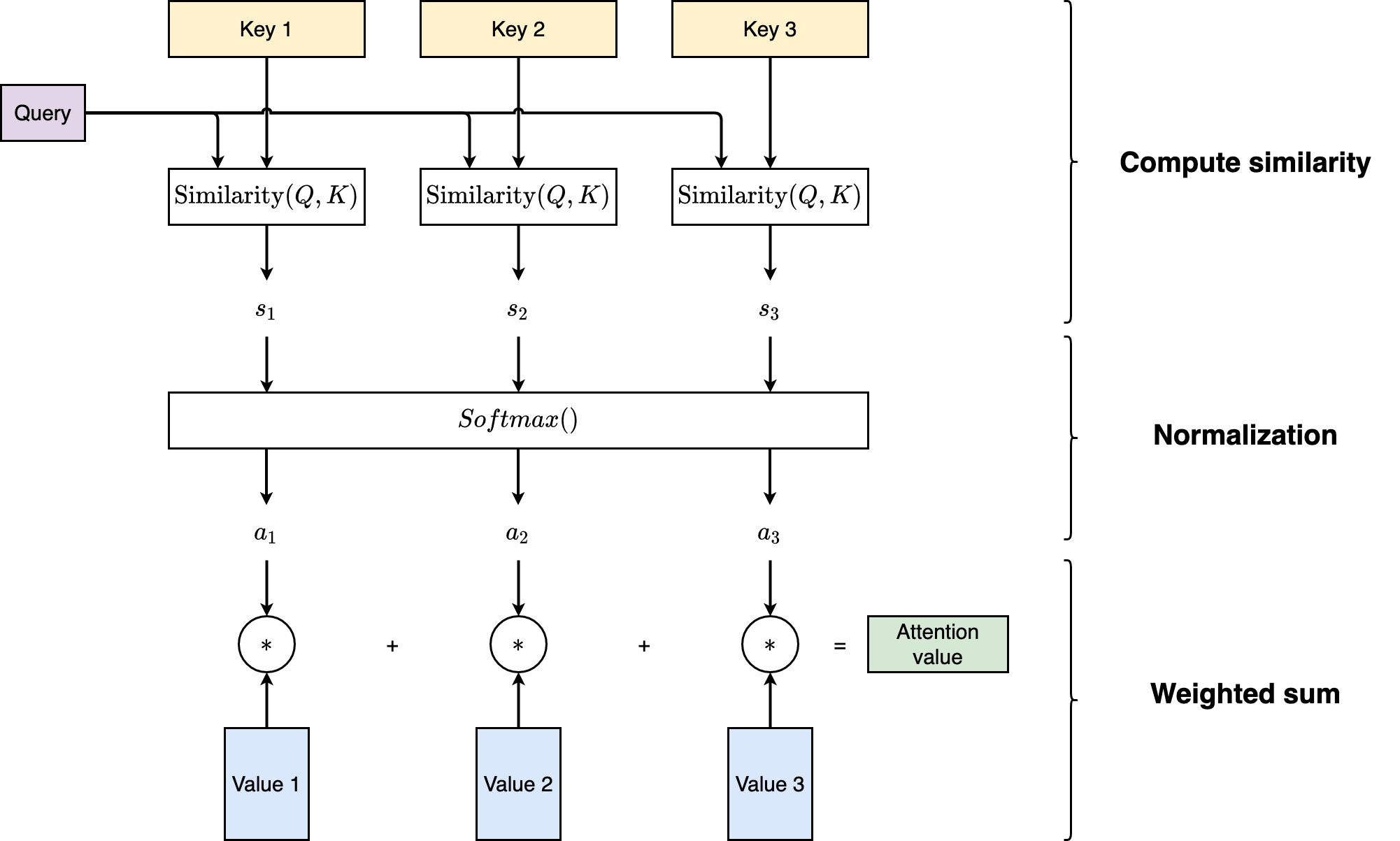
Computation of attention
Compute similarity/relevance score between query $Q$ and each key $K\_i$ using one of the following methods
Dot product
$$ s\_i = \operatorname{Similarity}(Q, K\_i) = Q \cdot K\_i $$Cosine similarity
$$ s\_i = \operatorname{Similarity}(Q, K\_i) = \frac{Q \cdot K\_i}{\\|Q\\| \cdot \\|K\_i\\|} $$MLP
$$ s\_i = \operatorname{Similarity}(Q, K\_i) = \operatorname{MLP}(Q, K\_i) $$
Apply $softmax()$, obtain weight for each value $V\_i$
$$ a\_i = \frac{e^{s\_i}}{\sum\_{j=1}^{N} e^{s\_j}} \in [0, 1] $$ $$ \sum\_{i} a\_i = 1 $$Weighted sum
$$ \operatorname{Attention}(Q, \text{Source}) = \sum\_{i}^{N} a\_i V\_i $$
Self-Attention
In general Encoder-Decoder architecture, source (input) and target (output) are different. For example, in French-English translation task, source is the input frence sentence, and target is the output translated english sentence. In this case, query comes from target. Attention mechanism is applied between query and elements in source.
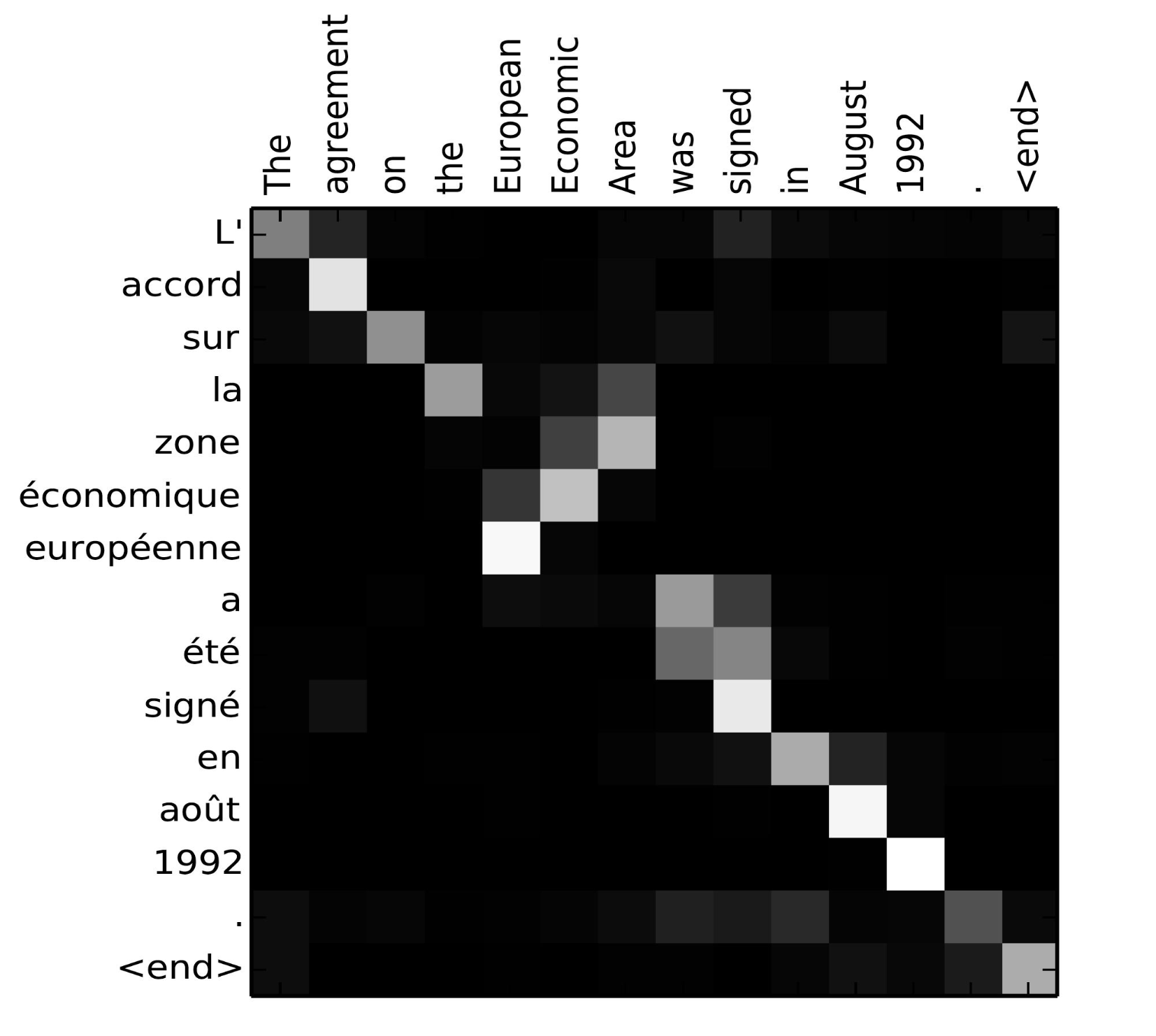
Alignment matrix of ‘L’accord sur l’Espace économique européen a été signé en août 1992’ (French) and its English translation ‘The agreement on the European Economic Area was signed in August 1992’. In this case, source is the Frence sentence and target is the English sentence. (Source: Bahdanau et al., 2015)
A special case is that source and target are the SAME. This is called self-attention, also known as intra-attention. It is an attention mechanism relating different positions of a single sequence in order to compute a representation of the same sequence. In other words, $Q=K=V$.
The self-attention answers the question: “Looking at a word in a sentence, how much attention should be paid to each of the other words in this sentence?”
Example: In this paper, self-attention is applied to do machine reading. the self-attention mechanism enables us to learn the correlation between the current words and the previous part of the sentence.

The current word is in red and the size of the blue shade indicates the activation level. (Source: Cheng et al., 2016)
Self-Attention in Detail
Assume that we have 4 input vector $\boldsymbol{a_{1}},..., \boldsymbol{a_{4}}$. As an exmple, we take the first output, $b_{1}$, to see how self-attention works under the hood.
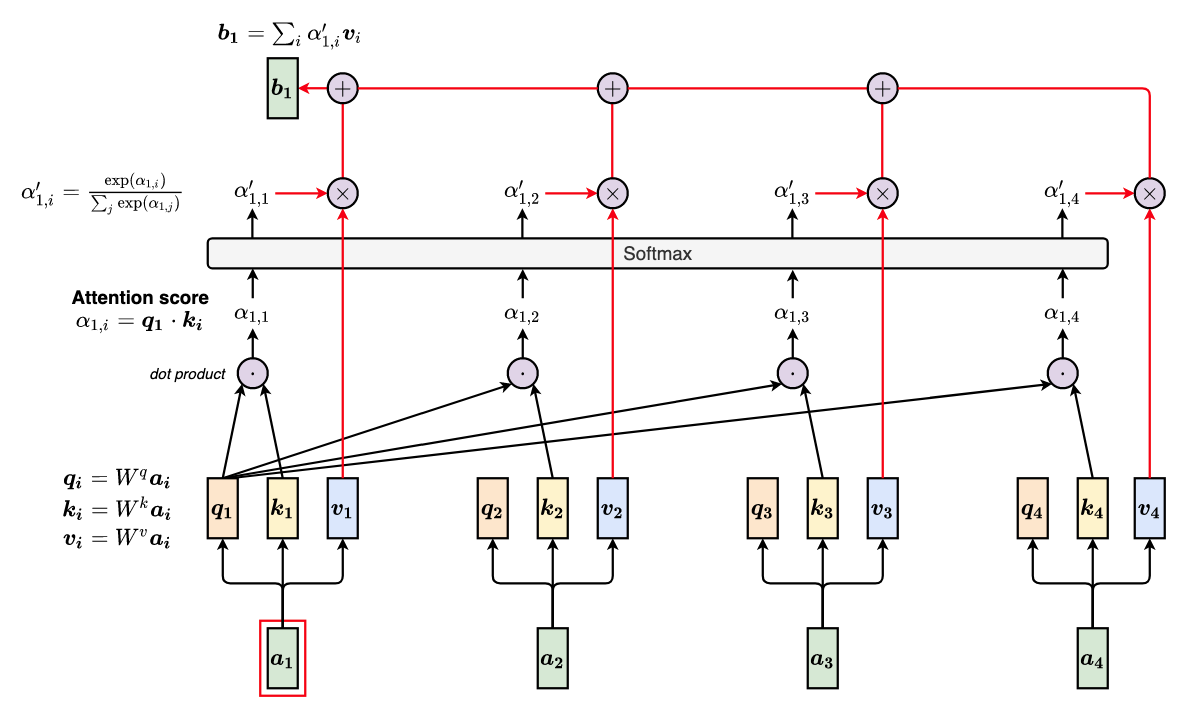
Self-attention computation
For every input vector $\boldsymbol{a}\_i$, we apply 3 learnable linear transformation (i.e., three matrix $W^q, W^k, W^v$) to achieve the query, key, and value vectors
$$ \begin{array}{l} \forall a\_i: & \boldsymbol{q\_i} = W^q \boldsymbol{a\_i} \quad \text{(Query)}\\\\ & \boldsymbol{k\_i} = W^k \boldsymbol{a\_i} \quad \text{(Key)}\\\\ & \boldsymbol{v\_i} = W^v \boldsymbol{a\_i} \quad \text{(Value)} \end{array} $$We’re looking at the first input vector $\boldsymbol{a_{1}}$. We compute attention scores $\alpha\_{1, i}$ by performing dot product of $\boldsymbol{q_{1}}$ and $\boldsymbol{k_{i}}$.
$$ \alpha\_{1, i} = \boldsymbol{q_1} \cdot \boldsymbol{k_i} $$$\alpha\_{1, i}$ can also be considered as the similarity/relevance between $\boldsymbol{q_1}$ and $\boldsymbol{k_i}$
We perform Normalization for the attention score by applying Softmax function.
$$ \alpha\_{1, i}^\prime = \frac{\exp(\alpha\_{1, i})}{\sum\_j \exp(\alpha\_{1, j})} $$$\alpha\_{1, i}^\prime$ is the weight of attention that should be paid to the vector $\boldsymbol{a}\_i$ when looking at the vector $\boldsymbol{a}\_1$
We extract information based on the normalized attention scores by performing a weighted sum of $\boldsymbol{v\_i}$
$$ \boldsymbol{b\_1} = \sum\_{i} \alpha\_{1, i}^\prime \boldsymbol{v}\_i $$
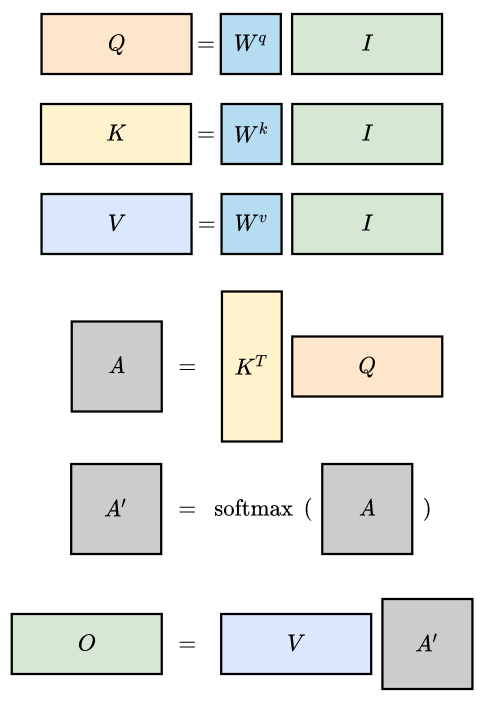
Matrix Representation
The illustration above shows the details of self-attention computation. In practice, we use matrix multiplication to make the computation more efficient.
Get query, key, value vectors
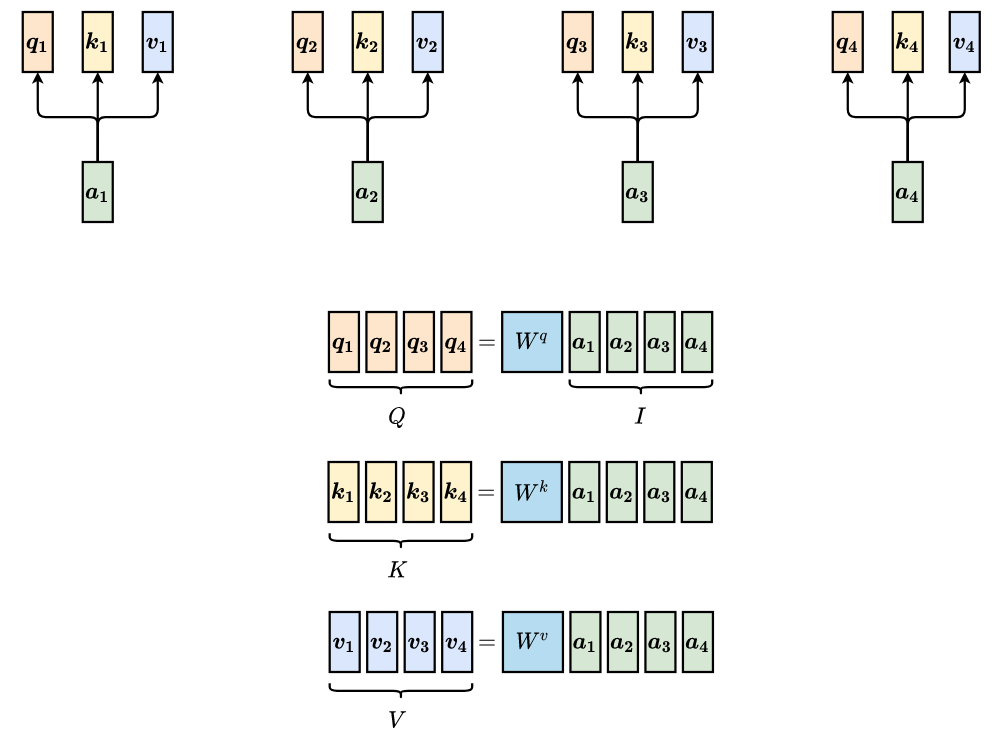
Compute attention scores
- For $\alpha_{1, i}$:
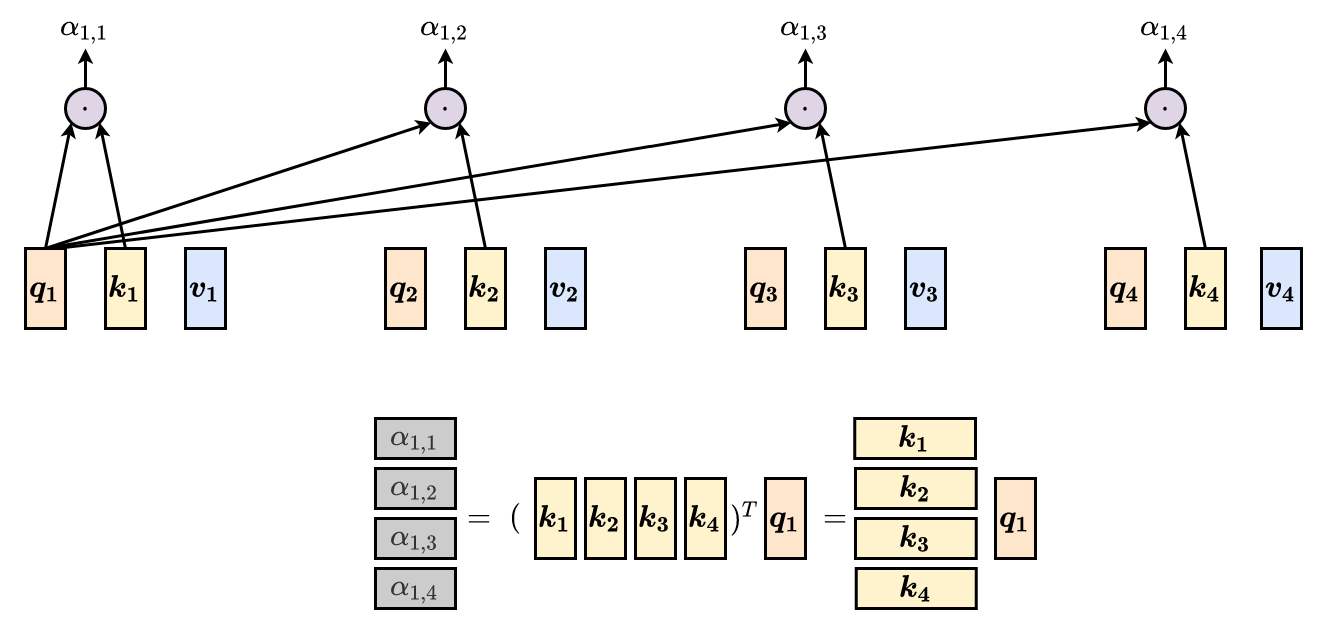
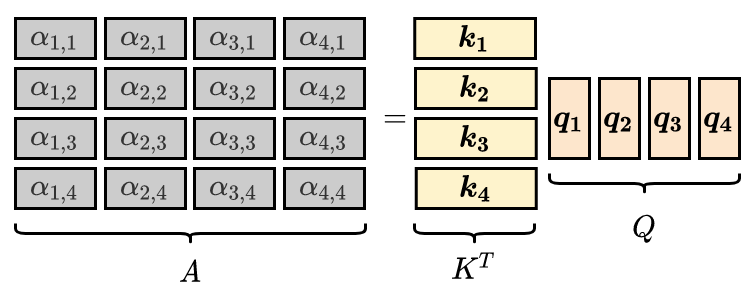
For all attention scores:
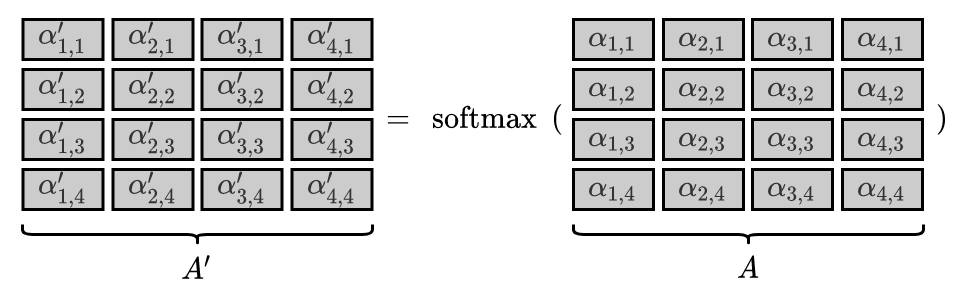
Apply softmax:
Compute weighted sum of $\boldsymbol{v}\_i$
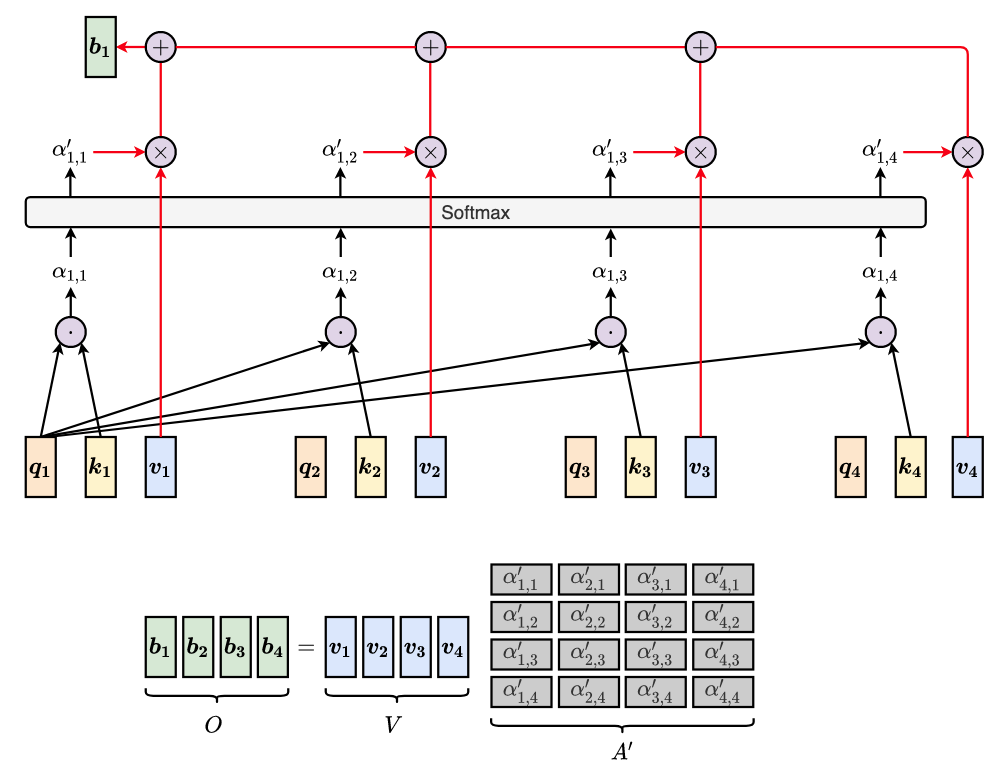
In summary:
Multi-head Self-Attention
We take 2 heads as example:
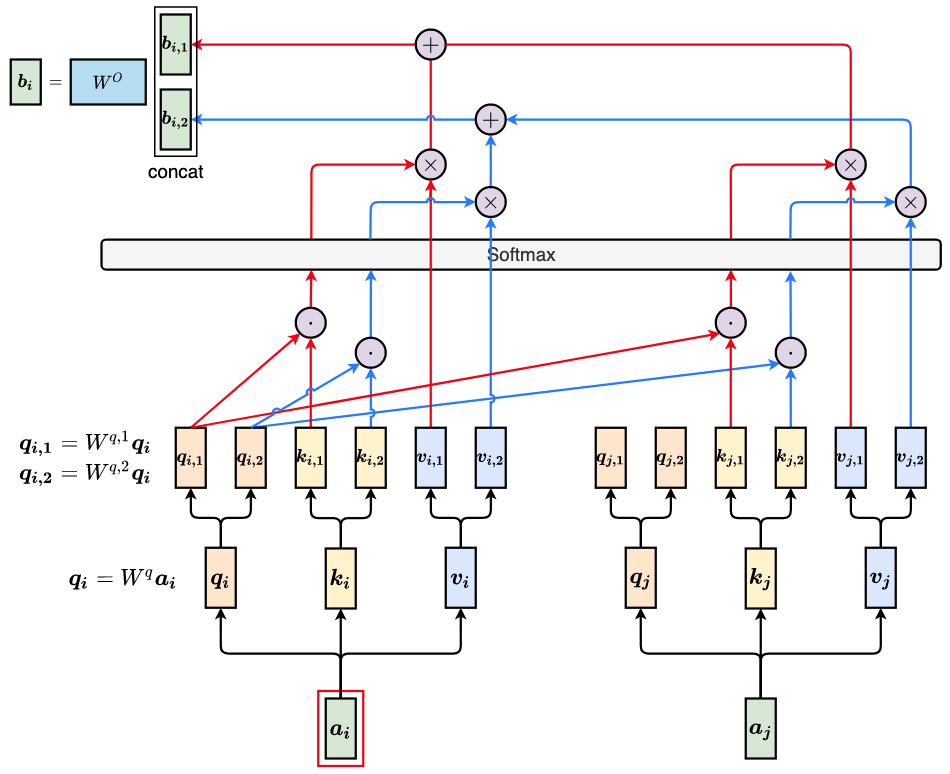
Multi-head Self-attention (2 heads as example)
Different heads represent different types of relevance. Multi-head attention allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions.
Self-Attention for Image
The required input of self-attention is a vector set. An image can also be considered as a vector set.
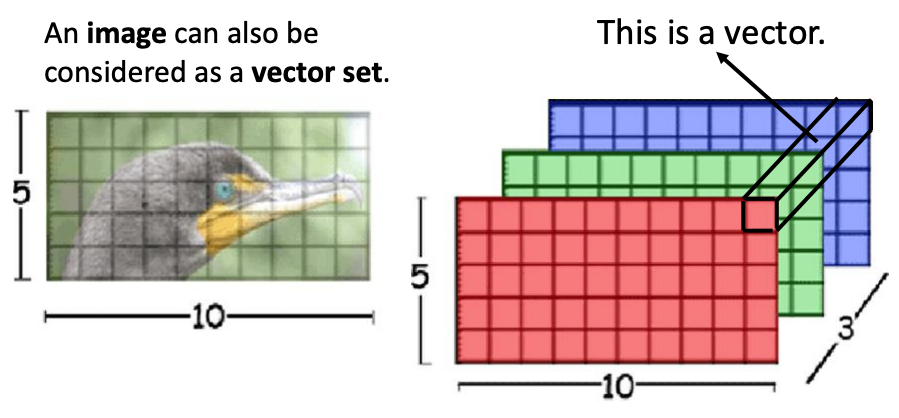
This image can be considered as a vector set containing $5 \times 10$ vectors of shape $(1 \times 1 \times 3).$
Self-Attention vs. CNN
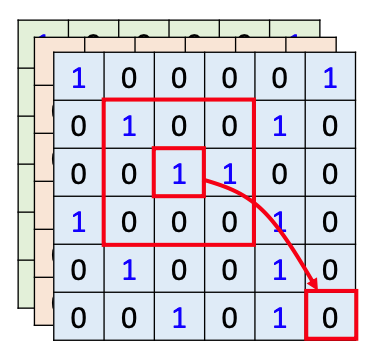
CNN: Self-attention can only only attends in a fixed local receptive field
$\Rightarrow$ CNN is simplified self-attention
Self-attention: CNN with learnable receptive field
- Can consider information of the whole image $\Rightarrow$ More flexible than CNN
- The receptive field is learnable.
$\Rightarrow$ Self-attention is the complex version of CNN
For a more detailed and mathematical explanation, see paper On the Relationship between Self-Attention and Convolutional Layers, as well as their blog post and visualization.
Reference
- 深度学习中的注意力机制(2017版) - explains attention mechanism intuitively and detailedly
- Attention? Attention! - Summary of attention mechanisms
- 📹 【機器學習2021】自注意力機制 (Self-attention) (上)
- 📹 【機器學習2021】自注意力機制 (Self-attention) (下)