Annotation Conversion: COCO JSON to YOLO Txt
Bounding box formats comparison and conversion
In COCO Json, the format of bounding box is:
"bbox": [
<absolute_x_top_left>,
<absolute_y_top_left>,
<absolute_width>,
<absolute_height>
]
However, the annotation is different in YOLO. For each .jpg image, there’s a .txt file (in the same directory and with the same name, but with .txt-extension). This .txt file holds the objects and their bounding boxes in this image (one line for each object), in the following format 1:
<object-class> <relative_x_center> <relative_y_center> <relative_width> <relative_height>
<object-class>: integer number of object from0to(classes-1)<relative_x_center> <relative_y_center> <relative_width> <relative_height>float values relative to width and height of image (equal from (0.0 to 1.0])
For example, for img1.jpg there should be img1.txt containing something looks like followings:
1 0.716797 0.395833 0.216406 0.147222
0 0.687109 0.379167 0.255469 0.158333
2 0.420312 0.395833 0.140625 0.166667
The following figure illustrates the difference of bounding box annotation between COCO and YOLO:
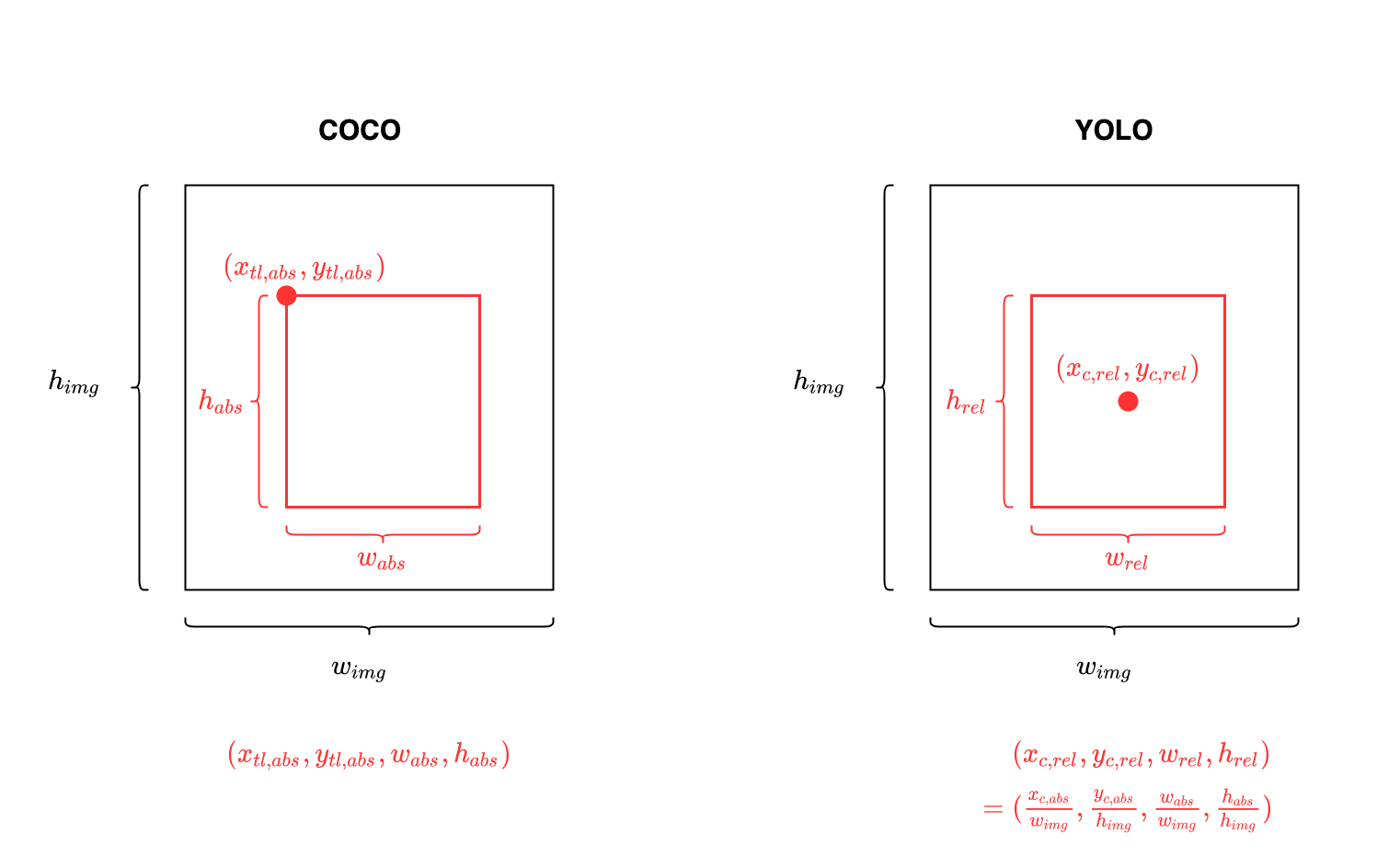
Bounding box format: COCO vs YOLO
Convert the bounding box annotation format from COCO to YOLO:
$$ \begin{array}{ll} x\_{yolo} &= (x\_{coco} + \frac{w\_{coco}}{2}) / w\_{img} \\\\ y\_{yolo} &= (y\_{coco} + \frac{h\_{coco}}{2}) / h\_{img} \\\\ w\_{yolo} &= w\_{coco} / w\_{img} \\\\ h\_{yolo} &= h\_{coco} / h\_{img} \end{array} $$def convert_bbox_coco2yolo(img_width, img_height, bbox):
"""
Convert bounding box from COCO format to YOLO format
Parameters
----------
img_width : int
width of image
img_height : int
height of image
bbox : list[int]
bounding box annotation in COCO format:
[top left x position, top left y position, width, height]
Returns
-------
list[float]
bounding box annotation in YOLO format:
[x_center_rel, y_center_rel, width_rel, height_rel]
"""
# YOLO bounding box format: [x_center, y_center, width, height]
# (float values relative to width and height of image)
x_tl, y_tl, w, h = bbox
dw = 1.0 / img_width
dh = 1.0 / img_height
x_center = x_tl + w / 2.0
y_center = y_tl + h / 2.0
x = x_center * dw
y = y_center * dh
w = w * dw
h = h * dh
return [x, y, w, h]
Convert COCO JSON to YOLO txt
The structure of training set in COCO format is:
- train
|- _annotations.coco.json
|- img_001.jpg
|- img_002.jpg
|- img_003.jpg
...
_annotations.coco.json contains all information about the dataset, images, and annotations. (More see: COCO JSON Format for Object Detection)
The structure of training set in YOLO format is:
- train
|- _darknet.labels
|- img_001.jpg
|- img_001.txt
|- img_002.jpg
|- img_002.txt
|- img_003.jpg
|- img_003.txt
...
_darknet.labelscontains objects names, each in new line- For each
.jpgimage there’s a corresponding.txtfile with the same name
Now we create .txt file for each image based on _annotations.coco.json:
import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
import shutil
def make_folders(path="output"):
if os.path.exists(path):
shutil.rmtree(path)
os.makedirs(path)
return path
def convert_coco_json_to_yolo_txt(output_path, json_file):
path = make_folders(output_path)
with open(json_file) as f:
json_data = json.load(f)
# write _darknet.labels, which holds names of all classes (one class per line)
label_file = os.path.join(output_path, "_darknet.labels")
with open(label_file, "w") as f:
for category in tqdm(json_data["categories"], desc="Categories"):
category_name = category["name"]
f.write(f"{category_name}\n")
for image in tqdm(json_data["images"], desc="Annotation txt for each iamge"):
img_id = image["id"]
img_name = image["file_name"]
img_width = image["width"]
img_height = image["height"]
anno_in_image = [anno for anno in json_data["annotations"] if anno["image_id"] == img_id]
anno_txt = os.path.join(output_path, img_name.split(".")[0] + ".txt")
with open(anno_txt, "w") as f:
for anno in anno_in_image:
category = anno["category_id"]
bbox_COCO = anno["bbox"]
x, y, w, h = convert_bbox_coco2yolo(img_width, img_height, bbox_COCO)
f.write(f"{category} {x:.6f} {y:.6f} {w:.6f} {h:.6f}\n")
print("Converting COCO Json to YOLO txt finished!")
Example
Assuming we have a COCO Json file _annotations.coco.json:
{
"info": {
"year": "2020",
"version": "1",
"description": "Exported from roboflow.ai",
"contributor": "Roboflow",
"url": "https://app.roboflow.ai/datasets/hard-hat-sample/1",
"date_created": "2000-01-01T00:00:00+00:00"
},
"licenses": [
{
"id": 1,
"url": "https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/",
"name": "Public Domain"
}
],
"categories": [
{
"id": 0,
"name": "Workers",
"supercategory": "none"
},
{
"id": 1,
"name": "head",
"supercategory": "Workers"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "helmet",
"supercategory": "Workers"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "person",
"supercategory": "Workers"
}
],
"images": [
{
"id": 0,
"license": 1,
"file_name": "0001.jpg",
"height": 275,
"width": 490,
"date_captured": "2020-07-20T19:39:26+00:00"
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"id": 0,
"image_id": 0,
"category_id": 2,
"bbox": [
45,
2,
85,
85
],
"area": 7225,
"segmentation": [],
"iscrowd": 0
},
{
"id": 1,
"image_id": 0,
"category_id": 2,
"bbox": [
324,
29,
72,
81
],
"area": 5832,
"segmentation": [],
"iscrowd": 0
}
]
}
convert_coco_json_to_yolo_txt("output", "_annotations.coco.json")
Categories: 100%|██████████| 4/4 [00:00<00:00, 2471.24it/s]
Annotation txt for each iamge: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1800.13it/s]
Converting COCO Json to YOLO txt finished!
An folder named output is created and has the structure:
- output
|- 0001.txt
|- _darknet.labels
Content of _darknet.labels:
Workers
head
helmet
person
Content of 0001.txt:
2 0.178571 0.161818 0.173469 0.309091
2 0.734694 0.252727 0.146939 0.294545