👍 Loss Functions
- Quantifies what it means to have a “good” model
- Different types of loss functions for different tasks, such as:
- Classification
- Regression
- Metric Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Classification
Classification: Predicting a discrete class label
Negative log-likelihood loss (per sample $x$) / Cross-Entropy loss
$$ L(\boldsymbol{x}, y)=-\sum\_{j} y_{j} \log p\left(c\_{j} \mid \boldsymbol{x}\right) $$- Used in various multiclass classification methods for NN training
Hinge Loss: used in Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
$$ L(x, y)=\sum\_{j} \max \left(0,1-x\_{i} y\_{i}\right) $$
Regression
Regression: Predicting a one or multiple continuous quantities $y_1, \dots, y\_n$
Goal: Minimize the distance between the predicted value $\hat{y}\_j$ and true values $y_j$
L1-Loss (Mean Average Error)
$$ L(\hat{y}, y)=\sum\_{j}\left(\hat{y}\_{j}-x\_{j}\right) $$L2-Loss (Mean Square Error, MSE)
$$ L(\hat{y}, y)=\sum\_{j}\left(\hat{y}\_{j}-x\_{j}\right)^2 $$
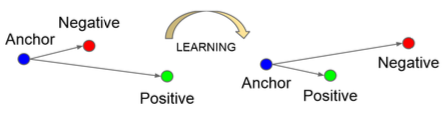
Metric Learning / Similarity Learning
A model for measuring the distance (or similarity) between objects
Triplet Loss
$$ \sum_{(a, p, n) \in T} \max \left\\{0, \alpha-\left\|\mathbf{x}\_{a}-\mathbf{x}\_{n}\right\|\_{2}^{2}+\left\|\mathbf{x}\_{a}-\mathbf{x}\_{p}\right\|\_{2}^{2}\right\\} $$