Data Augmentation
What is data augmentation?
To solve the problem that it’s hard to get enough data for training neural networks, image augmentation is a process of creating new training examples from the existing ones. To make a new sample, you slightly change the original image.
For instance, you could make a new image a little brighter; you could cut a piece from the original image; you could make a new image by mirroring the original one, etc. Here are some examples of transformations of the original image that will create a new training sample:
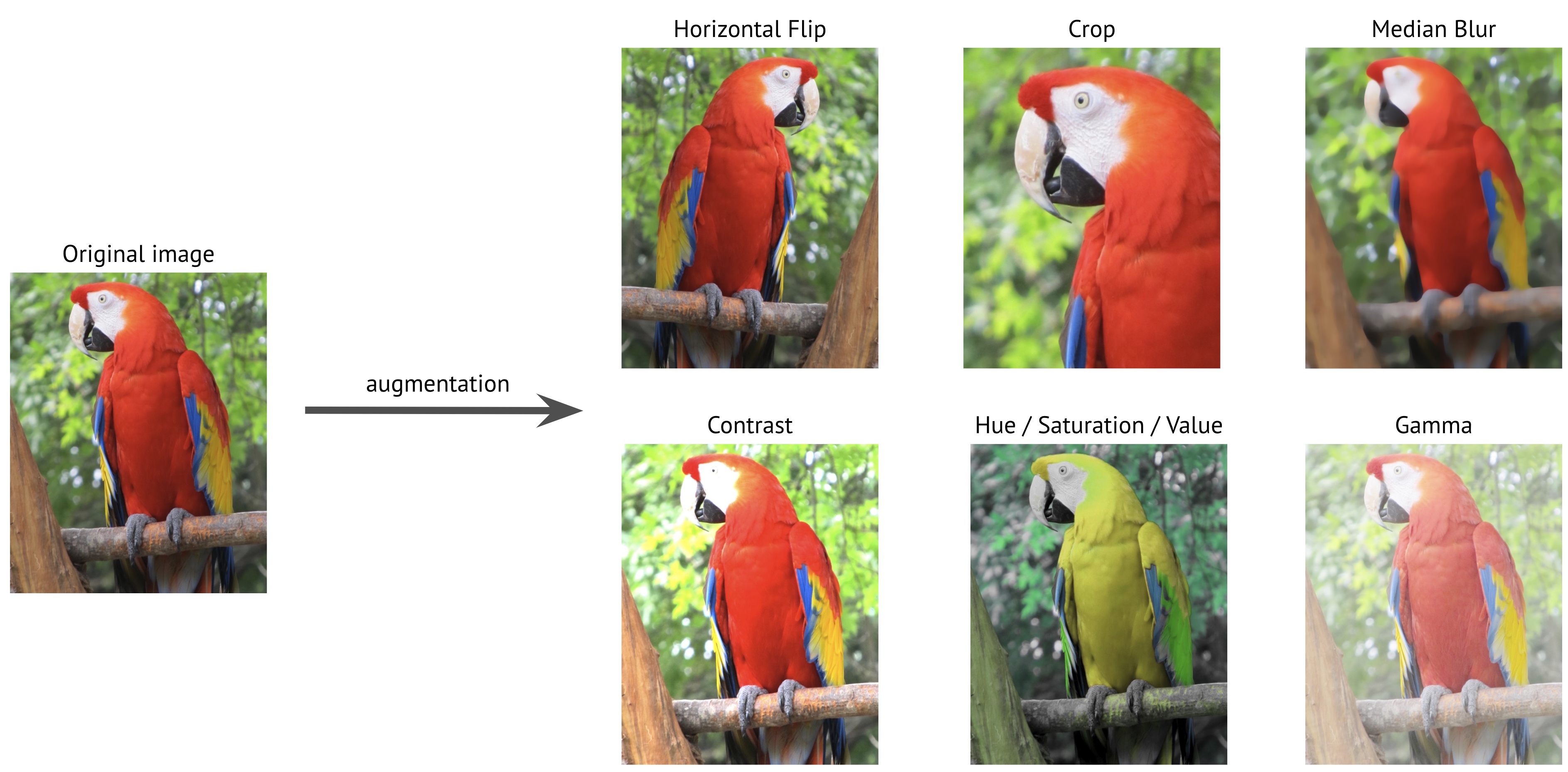
By applying those transformations to the original training dataset, you could create an almost infinite amount of new training samples.
Premise of data augmentation
A convolutional neural network that can robustly classify objects even if its placed in different orientations is said to have the property called invariance. More specifically, a CNN can be invariant to translation, viewpoint, size or illumination (Or a combination of the above).
When to apply augmentation?
The answer may seem quite obvious; we do augmentation before we feed the data to the model.
However, we have two options here:
- Offline augmentation
- Preferred for relatively smaller datasets
- Increasing the size of the dataset by a factor equal to the number of transformations we perform
- For example, by flipping all my images, I would increase the size of my odataset by a factor of 2
- Online augmentation / Augmentation on the fly
- Preferred for larger datasets, as we can’t afford the explosive increase in size.
- Perform transformations on the mini-batches that we would feed to our model.
Use data augmentation in the right way
‼️ Do NOT increase irrelevant data!!!
Sometimes not all augmentation techniques make sense for a dataset. Consider the following car example:

The first image (from the left) is the original, the second one is flipped horizontally, the third one is rotated by 180 degrees, and the last one is rotated by 90 degrees (clockwise).
They are pictures of the same car, but our target application may NEVER see cars presented in these orientations. For example, if we’re gonna classify random cars on the road, only the second image would make sense to be in the dataset.
How to conduct data augmentation in PyTorch?
Use torchvision.transforms
- Provides common image transformations
- Can be chained together using
transforms.Compose
🔥 Use albumentations
Demo
Demo for viewing different augmentation transformations
When will data augmentation be applied in PyTorch?
In any epoch the dataloader will apply a fresh set of random operations “on the fly”. I.e. the augmentation happens inside of this line:
for (data, target) in dataloader:
Instead of showing the exact same items at every epoch, you are showing a variant that has been changed in a different way. So after three epochs, you would have seen three random variants of each item in a dataset.
Note that each image will be transformed randomly on-the-fly, thus NO images will be generated and the length of Dataset stays the SAME.
If you want to perferm more augmentation and bring more varaibility for the dataset, just increase the number of epochs.
Reference: