Linked List
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
Draw It out!
To solve the linked list problems, the most important thing is to draw the linked list and the procedure out. The figure can help you to think and code.
2 Main Types of Problems
- Modification of links
- Concatenation of linked lists
To Be Noticed
Loops
When modifying links, it is easy to create loop uncarefully. To prevent this problem, draw the list out! With the help of figure, we can immediately notice and avoid loops.
Corner Cases
Common corner cases are
- Linked list is empty
- Linked list contains only one node
Techniques
Dummy Head
Add a
dummy_headbeforeheaddummy_head = ListNode(val=-1, next=head)
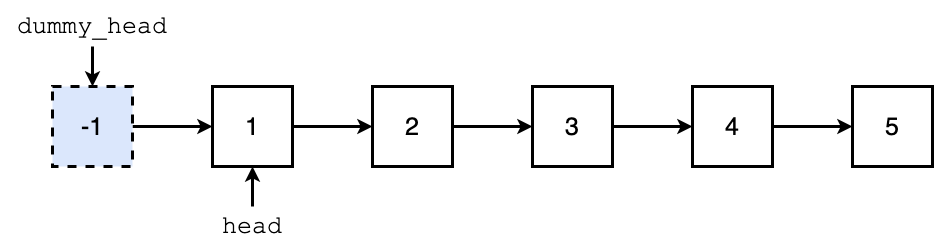
dummy_head.nextis always the first nodes after all operationsAdvantage of adding a
dummy_headis that we can treatheadas a normal node, which can help us to handle the corner cases easily (e.g. deletingheadnode)Leetcode problems
- 25
Fast and Slow pointers
Since linked list does not support random indexing as array, we have to access nodes starting from
headWe can use
fastandslowpointers to simulate the random access, e.g.- If we want to access the middle node of the linked list
fastandslowpointers start fromhead.- At each step,
slowmoves one step forward,fastmoves two steps forward - When
fastreaches the end,slowreaches the middle
- If we want to access the n-th node from the end
slowstarts fromhead,faststarts from the n-th node- At each step,
slowandfastmove one step forward - When
fastreaches the end,slowreaches n-th node from the end
- If we want to access the middle node of the linked list
Leetcode problems
Recursion
Linked list has the nature of recursion. If we master the idea of recursion, the solution will be suprisingly clean and succinct
To apply recursion, we just need to consider three questions
- Base case: Unter which situation / When should the recursion be ended?
- In linked list, base cases are empty list or list containing only one node
- Return value: What should be returned to the previous level?
- Goal of current level: What should be done in the current level?
Reference: 三道题套路解决递归问题
- Base case: Unter which situation / When should the recursion be ended?
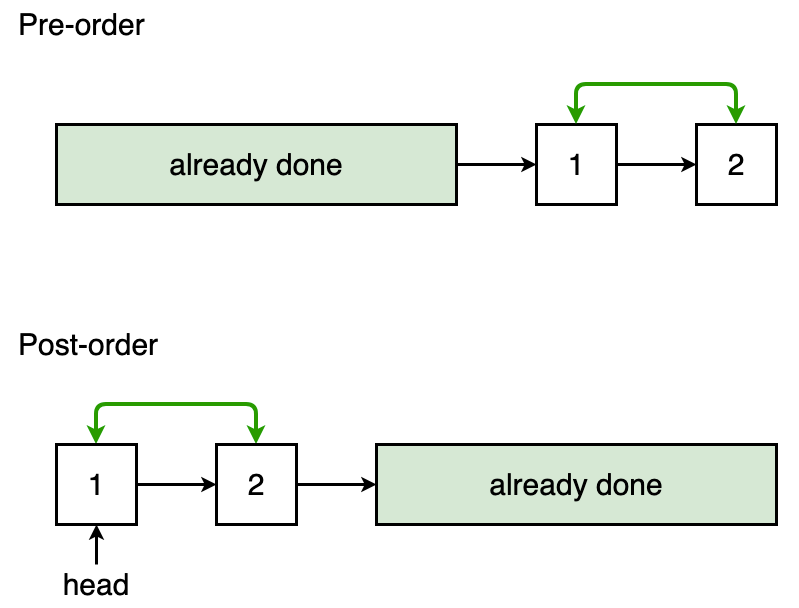
Pre-order traversal vs. post-orderrecursion
In pre-order traversal, we image that the previous nodes are already processed (we don’t care how they are processed)
In post-order traversal, we image that the nodes behind are already processed (we don’t care how they are processed)
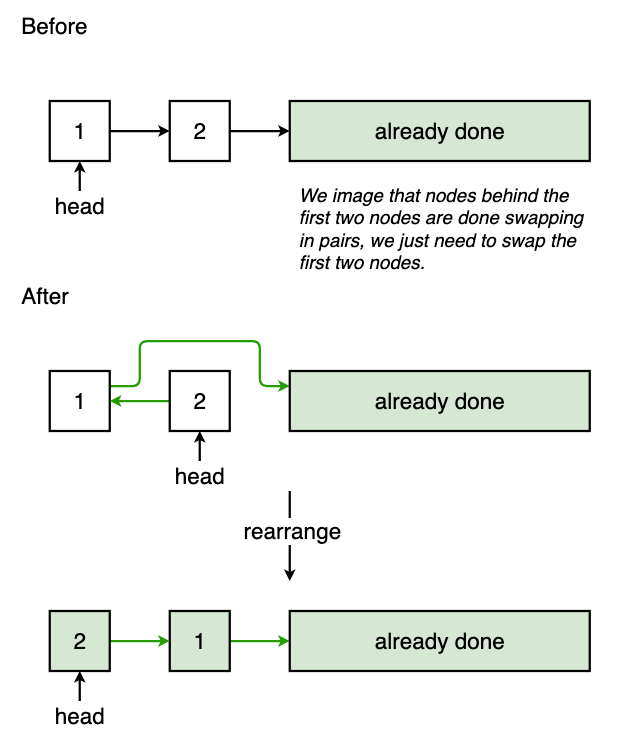
Example: Swap nodes in pairs
Example: 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
Leetcode problems
Sort Nodes Alphabetically When Modifying Links or Concatenating Nodes
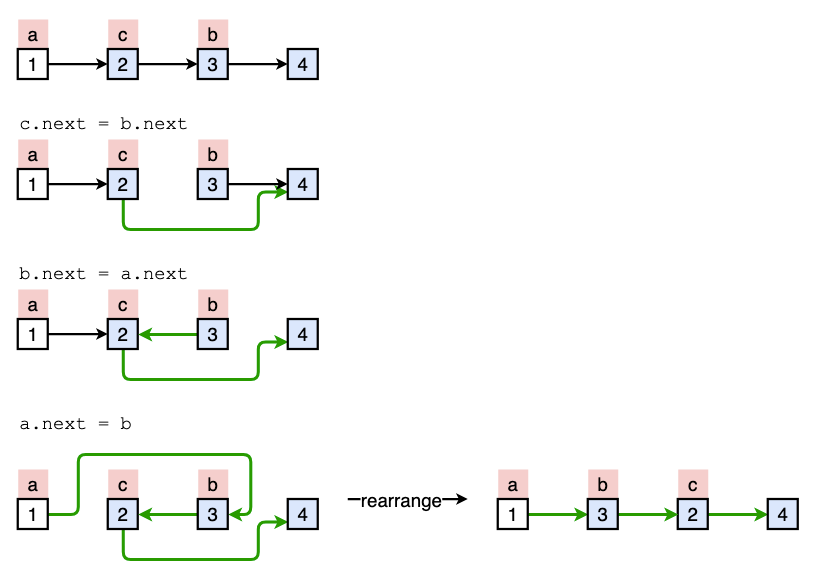
When modifying links or concatenating nodes, it’s easy to get lost or create loops uncarefully. A small trick to avoid these problems is to
- Draw out how the list looks like before and after modification
- Mark the order of nodes alphabetically
Example
We want to move node 3 to the front of node 2. We draw the “before and after” out:
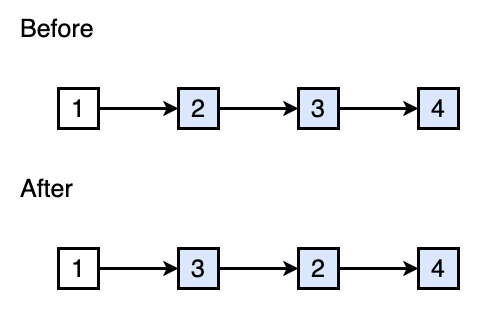
Then we mark the order of nodes alphabetically