Selection Sort
TL;DR
- Key idea: repeatedly selecting the smallest remaining item
- Time complexity: $O(n^2)$
Idea
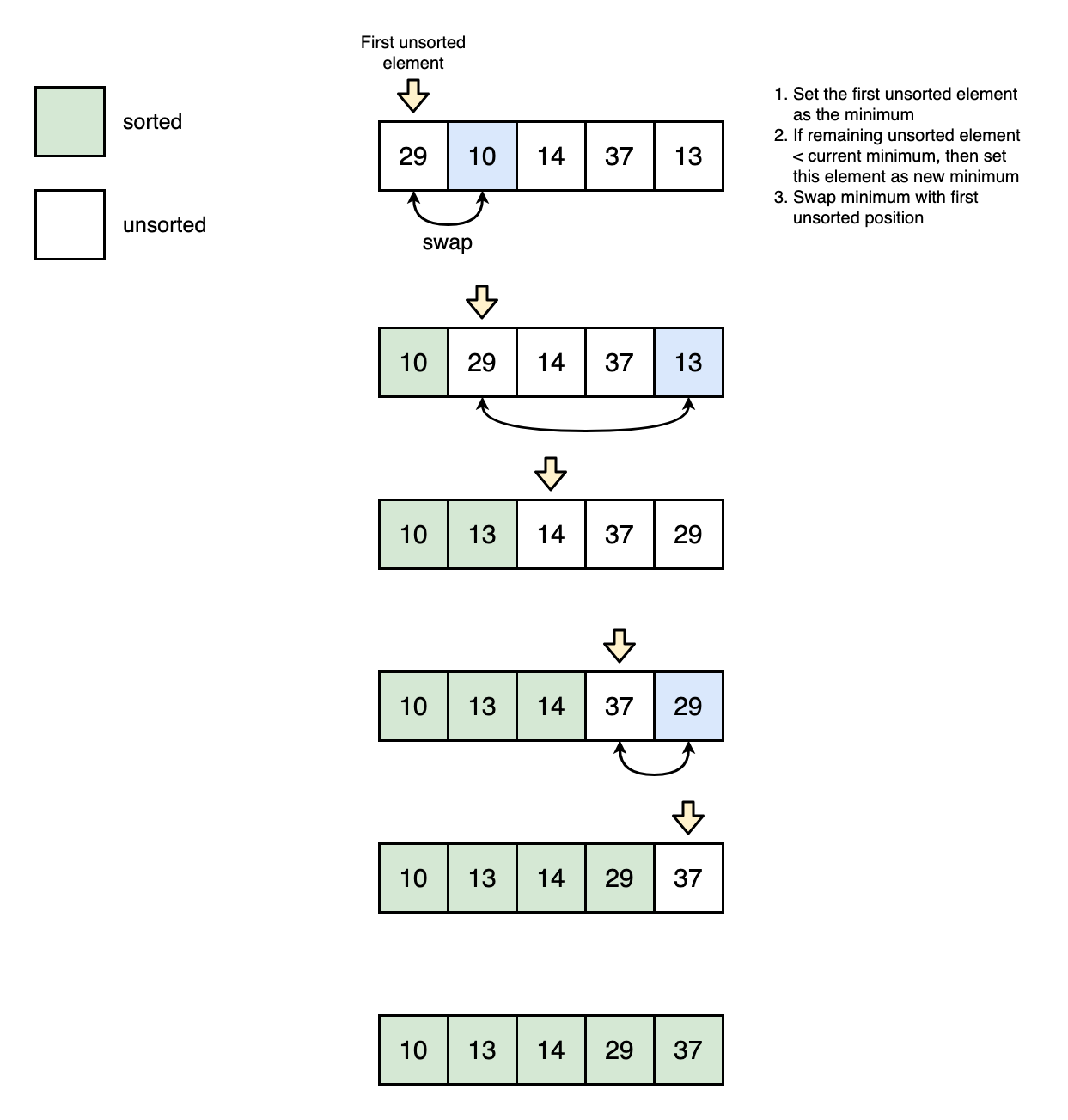
The idea of selection sort is pretty simple:
- First, find the smallest item in the array and exchange it with the first entry
- Then, find the next smallest item and exchange it with the sec- ond entry.
- Continue in this way until the entire array is sorted.
This method is called selection sort because it works by repeatedly selecting the smallest remaining item.
Pseudocode
repeat (len(arr) - 1) times:
set the first unsorted element as the current_minimum
for each of the unsorted elements:
if element < current_minimum:
set element as new minimum
swap minimum with first unsorted position
Complexity Analysis
Selection sort uses $\sim N^{2}/2$ compares and $N$ exchanges to sort an array of length $N$.
Therefore, time complexity is $O(n^2)$.
Python Implementation
In-place Implementation
def selection_sort_in_place(arr):
for i in range(len(arr)):
print(f"i = {i}")
print(f"Sorted part: {arr[:i]}, unsorted part: {arr[i:]}\n")
# Set the first unsorted element as current minimum
min_idx = i
# Check the remaining part:
# Is there an element which is smaller than the current minimum?
# If yes, then set this element as the new minimum
for j in range(i+1, len(arr)):
if arr[j] < arr[min_idx]:
min_idx = j
# If the first unsorted element is not the minimum,
# then swap it with the minimum
if i != min_idx:
arr[i], arr[min_idx] = arr[min_idx], arr[i]
return arr
arr = [37, 10, 14, 29, 13]
print(selection_sort_in_place(arr))
i = 0
Sorted part: [], unsorted part: [37, 10, 14, 29, 13]
i = 1
Sorted part: [10], unsorted part: [37, 14, 29, 13]
i = 2
Sorted part: [10, 13], unsorted part: [14, 29, 37]
i = 3
Sorted part: [10, 13, 14], unsorted part: [29, 37]
i = 4
Sorted part: [10, 13, 14, 29], unsorted part: [37]
[10, 13, 14, 29, 37]
Non In-place Implementation
def find_smallest(arr):
"""
Find the index of the smallest value in the array
"""
smallest_val = arr[0] # stores the smallest value
smallest_index = 0 # stores the index of the smallest value
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < smallest_val:
smallest_val = arr[i]
smallest_index = i
print(f"smallest val: {smallest_val}, smallest index: {smallest_index}")
return smallest_index
def selection_sort(arr):
new_arr = []
for i in range(len(arr)):
# Finds the smallest element in the array,
# and adds it to the new array
print(f"arr: {arr}")
smallest = find_smallest(arr)
new_arr.append(arr.pop(smallest))
print(f"new_arr: {new_arr} \n")
return new_arr
arr = [37, 10, 14, 29, 13]
print(f"sorted arr: {selection_sort(arr)}")
arr: [37, 10, 14, 29, 13]
smallest val: 10, smallest index: 1
new_arr: [10]
arr: [37, 14, 29, 13]
smallest val: 13, smallest index: 3
new_arr: [10, 13]
arr: [37, 14, 29]
smallest val: 14, smallest index: 1
new_arr: [10, 13, 14]
arr: [37, 29]
smallest val: 29, smallest index: 1
new_arr: [10, 13, 14, 29]
arr: [37]
smallest val: 37, smallest index: 0
new_arr: [10, 13, 14, 29, 37]
sorted arr: [10, 13, 14, 29, 37]