Gaußverteilung
Skalarer Fall (1D)
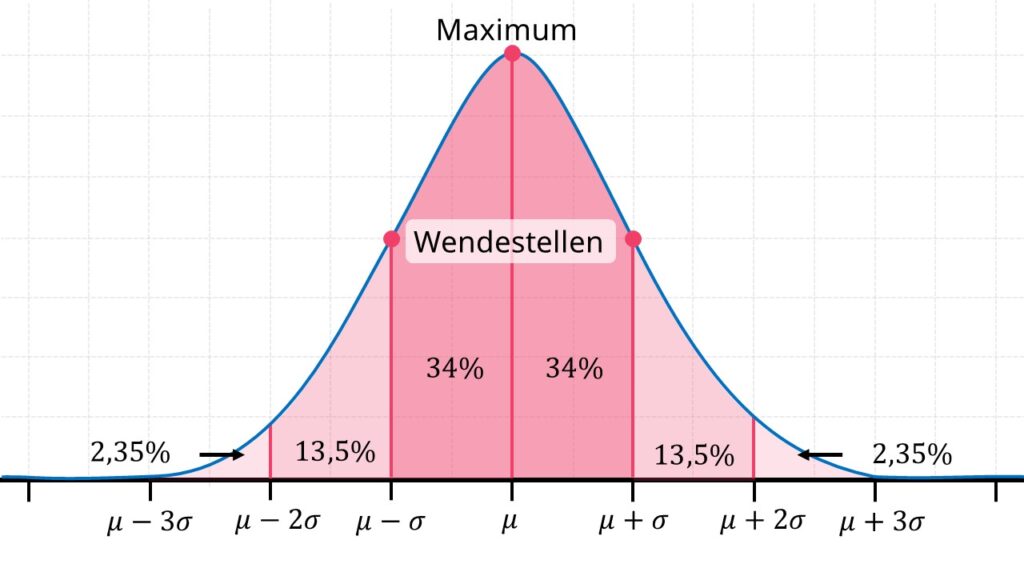 $$
f(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi} \sigma} \exp \left\{-\frac{1}{2} \frac{(x-\hat{x})^{2}}{\sigma^{2}}\right\}
$$
$$
f(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi} \sigma} \exp \left\{-\frac{1}{2} \frac{(x-\hat{x})^{2}}{\sigma^{2}}\right\}
$$Erwartungswert
$$ E_{f}\{x\}=\hat{x} $$Varianz
$$ E_{f}\left\{(x-\hat{x})^{2}\right\}=\sigma^{2} $$
Given the parameters $\mu$ and $\sigma$ of a Gaussian density, mean and variance are already given. On the other hand, assume that we wish to approximate a given density $\tilde{f}_x$ with a simpler density of the same mean and standard deviation. Then, given the mean and the standard deviation of the density $\tilde{f}_x$, an appropriate Gaussian density is immediately obtained. This is a property not generally shared by more complicated densities.
2D Normalverteilung
$$ \begin{aligned} f_{x y}(x, y)&=\frac{1}{2 \pi \sigma_{x} \sigma_{y} \sqrt{1-r^{2}}} \exp \left\{-\frac{1}{2} Q(x, y)\right\} \\ Q(x, y)&=\frac{1}{1-r}\left\{\frac{(x-\hat{x})^{2}}{\sigma_{x}^{2}}-2 r \frac{x-\hat{x}}{\sigma_{x}} \frac{y-\hat{y}}{\sigma_{y}}+\frac{(y-\hat{y})^{2}}{\sigma_{y}^{2}}\right\} \end{aligned} $$- $r \in [-1, 1]$: Korrelationskoeffizent (in some literature also written as $\rho$)
Alternativ
$$ f_{x y}(x, y)=\mathcal{N} \left(\left[\begin{array}{l} x \\ y \end{array}\right],\left[\begin{array}{l} \hat{x} \\ \hat{y} \end{array}\right],\left[\begin{array}{ll} C_{x x} & C_{x y} \\ C_{y x} & C_{y y} \end{array}\right]\right) $$mit
$$ \left[\begin{array}{ll} c_{x x} & c_{x y} \\ c_{y x} & c_{y y} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{lc} \sigma_{x}^{2} & r \sigma_{x} \sigma_{y} \\ r \sigma_{x} \sigma_{y} & \sigma_{y}^{2} \end{array}\right] $$Correlationskoeffizient
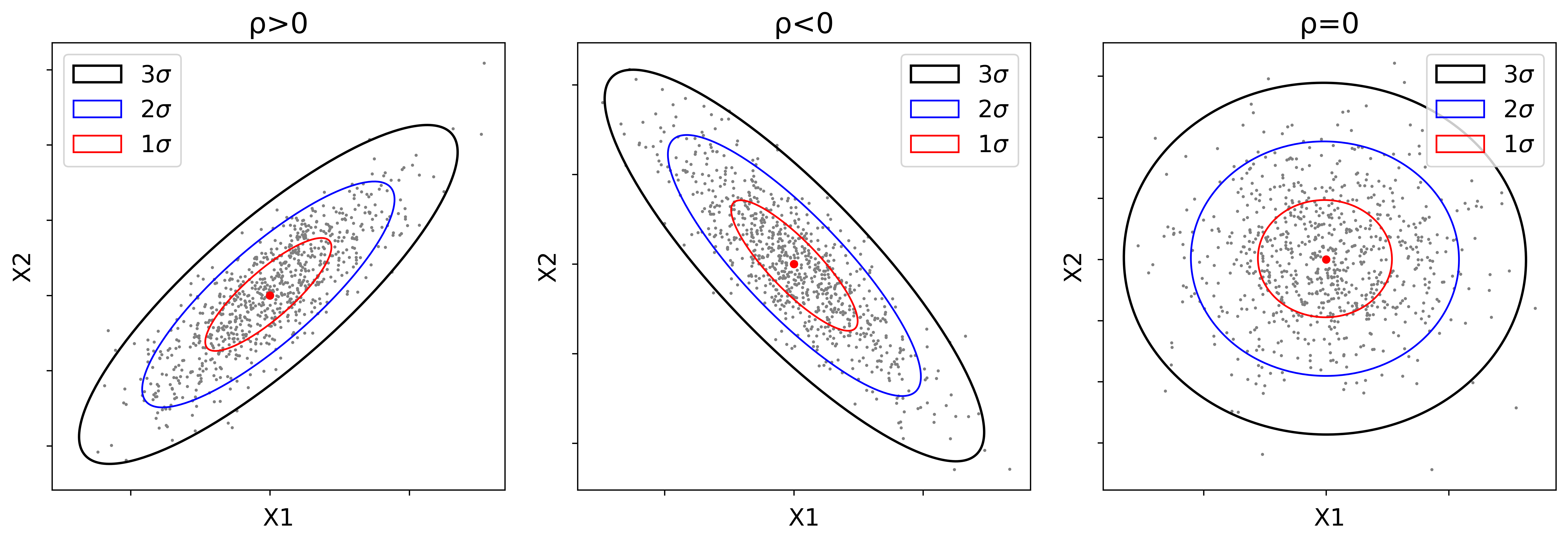
Correlation of bivariate Gaussian distribution ($\rho$ is the correlation coefficient). (Source: )
unkorreliert ($r = 0$) (Figure 1 right)
- $\Rightarrow \boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{y}$ unkorreliert
- $\Rightarrow$ (nur für Gauß) $\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{y}$ unabhängig ($f_{\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{y}} = f_{\boldsymbol{x}}(x) f_{\boldsymbol{y}}(y)$ )
positiv korreliert ($r > 0$) (Figure 1 left)
positiv korreliert ($r < 0$) (Figure 1 middle)
$N$-dim. Normalverteilung
$$ f_{\boldsymbol{x}}(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{(2 \pi)^{N} \cdot|\mathbf{C}|}} \exp \left\{-\frac{1}{2}(\underline{x}-\underline{\hat{x}})^{\top} \mathbf{C}^{-1}(\underline{x}-\underline{\hat{x}})\right\} $$- $\underline{\hat{x}}$ : Mean
- $\mathbf{C}$ : Kovarianzmatrix