Circuit Switching Vs. Packet Switching
TL;DR
| Switching Network | Characteristics | Suitable for | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circuit Switching | A dedicated channel or circuit is established for the duration of communications | Communications which require data to be transmitted in real time | Traditional telephone calls |
| Packet Switching | Connected through many routers, each serving different segment of network | More flexible and more efficient if some amount of delay is acceptable | Handles digital data |
Circuit Switching
A dedicated channel or circuit is established for the duration of communications.
The method used by the old traditional telephone call, carried over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
Also referred to as the Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS)
Ideal for communications which require data to be transmitted in real time
Normally used for traditional telephone calls
This is what a typical traditional telephone network look like.
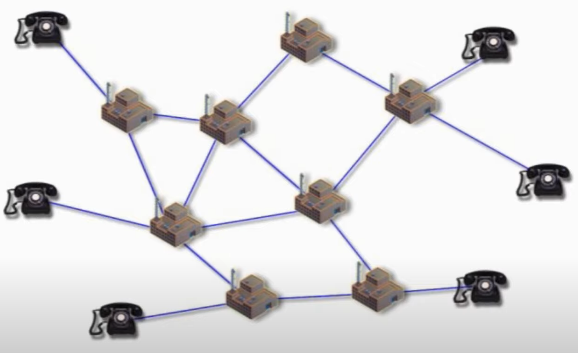
The PSTN networks are connected through central offices, which act as telephone exchanges, each serving a certain geographical area.
When person A calls Person B:
Packet Switching
Packet switching networks are connected through many routers, each serving different segment of networks
How it works?
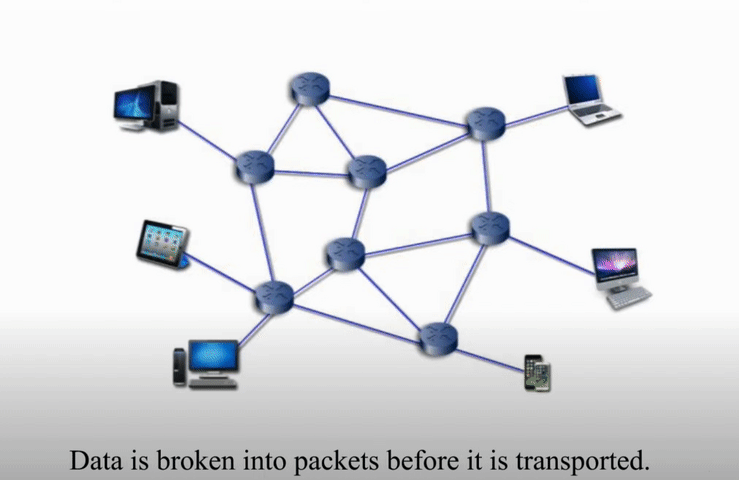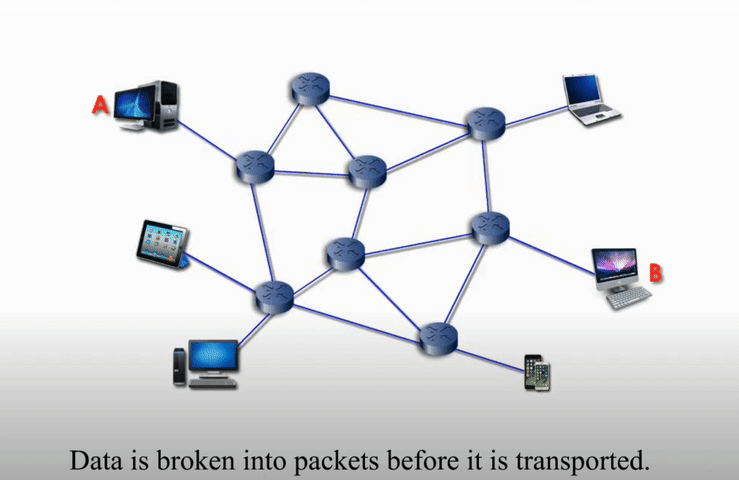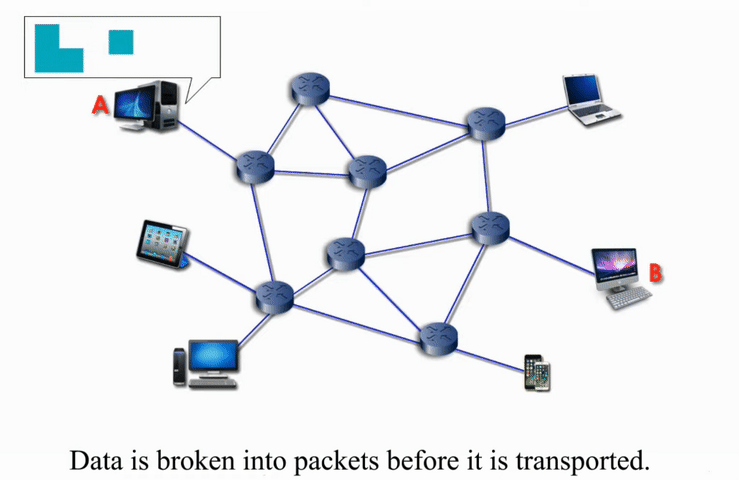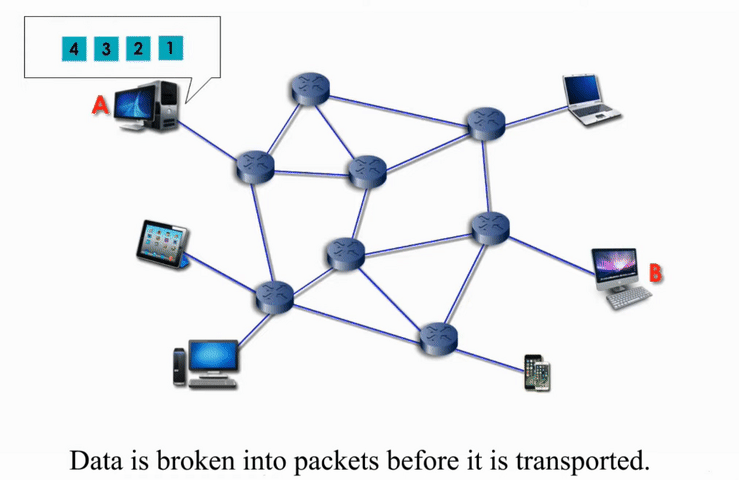
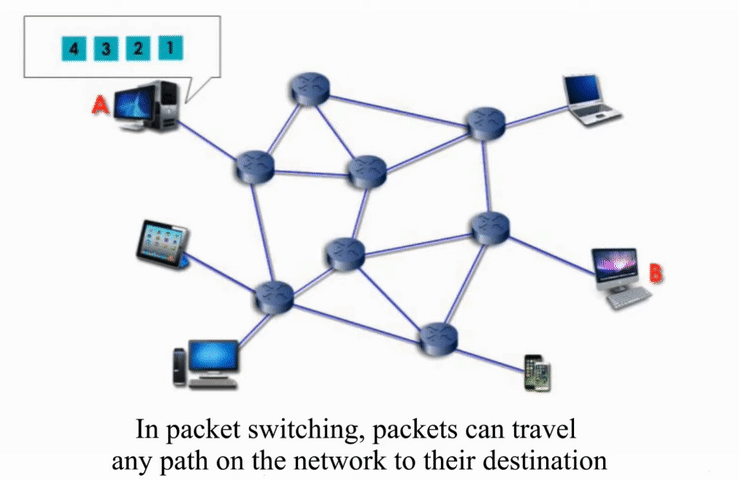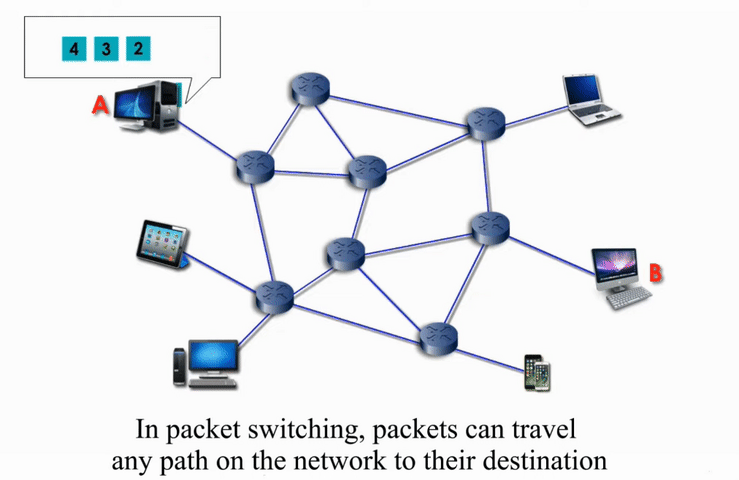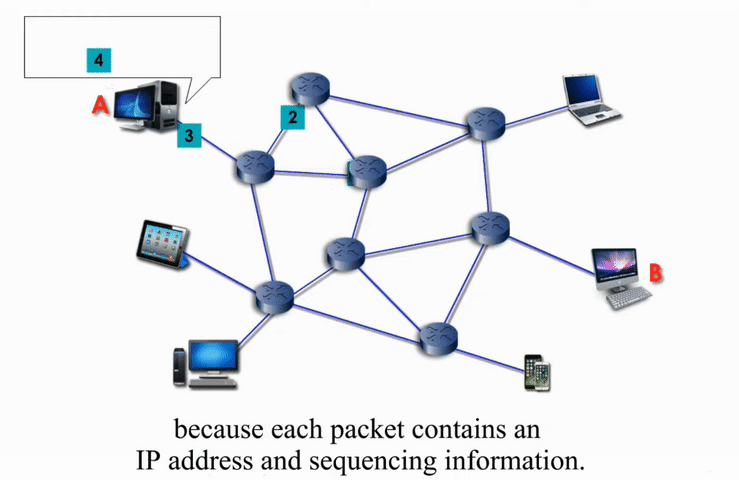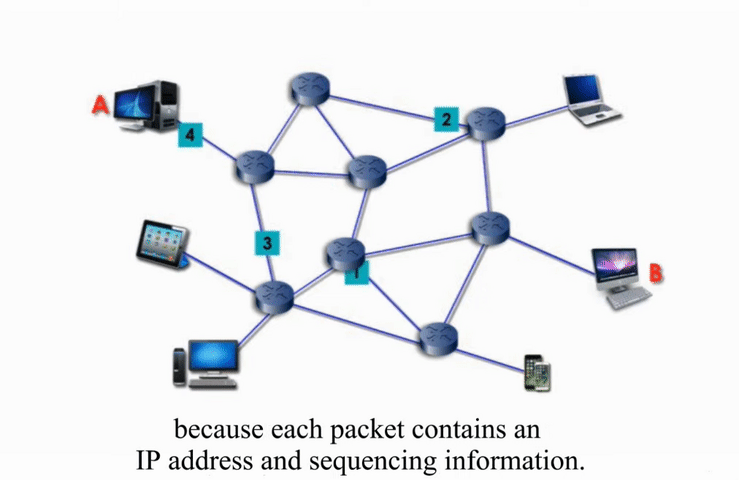
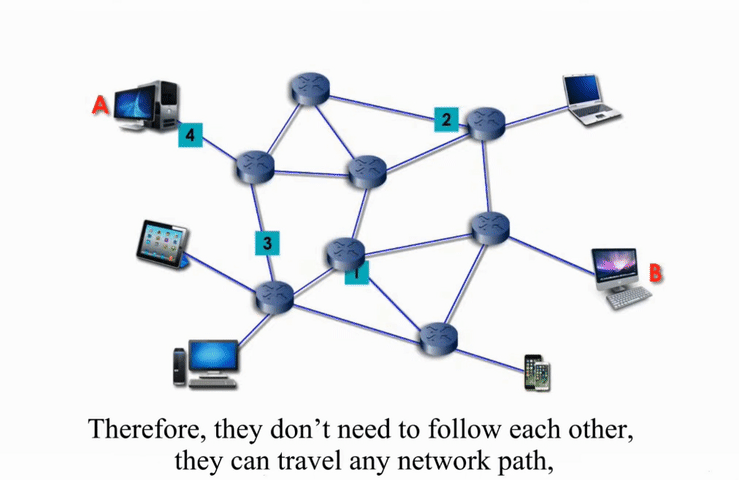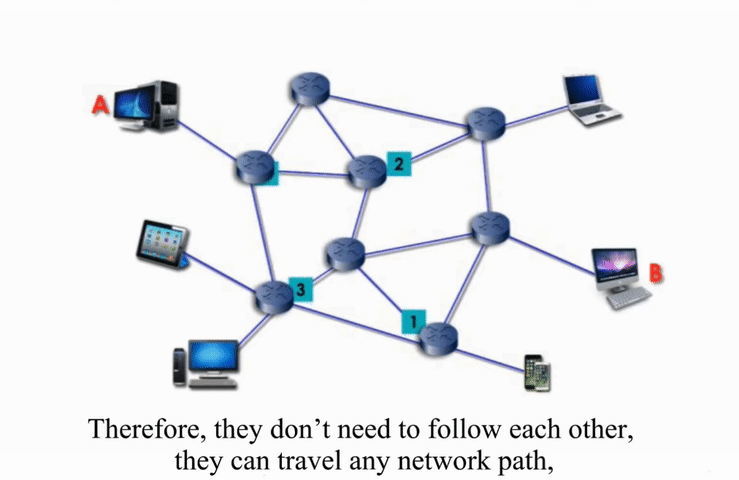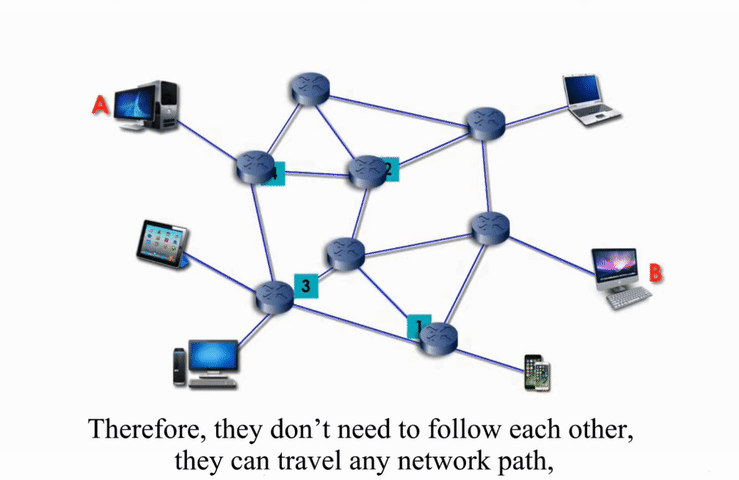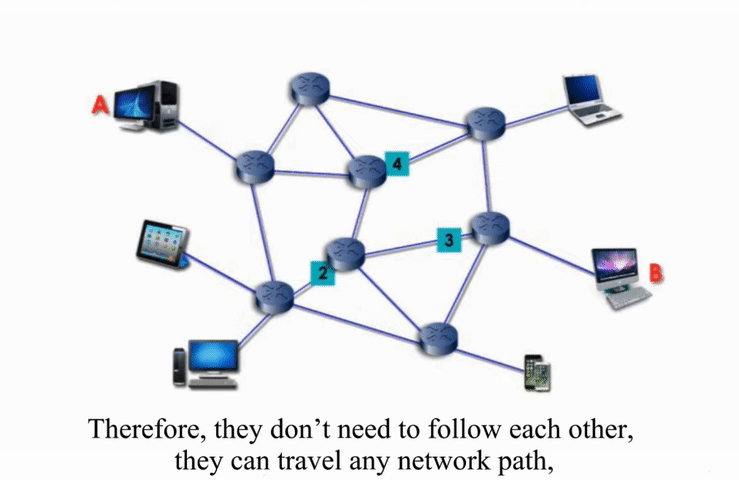
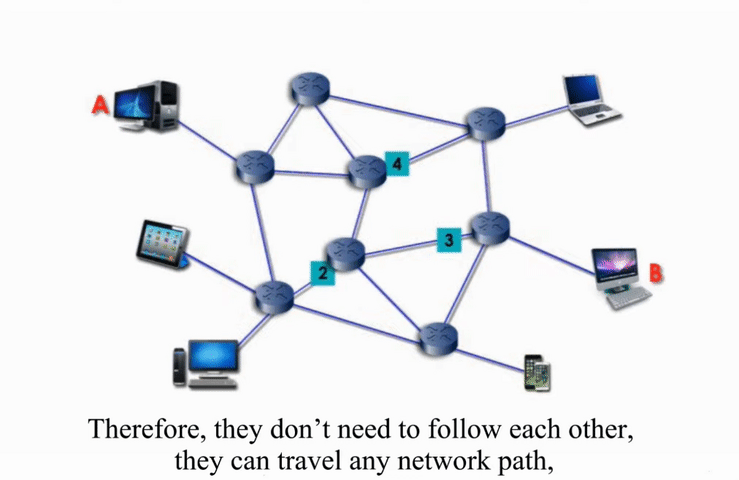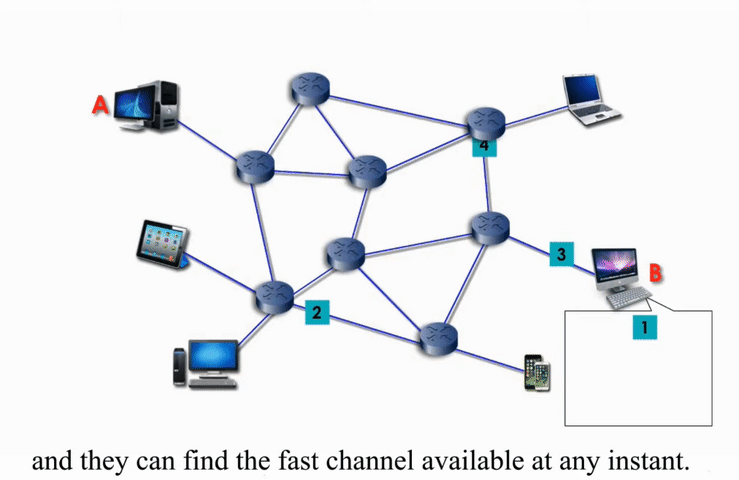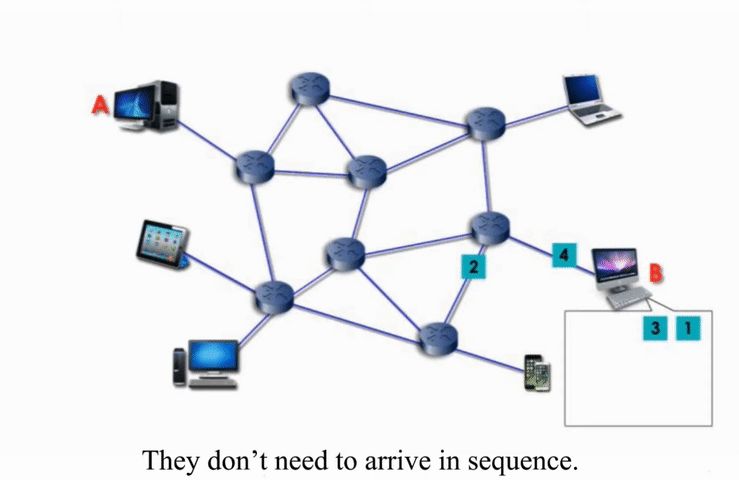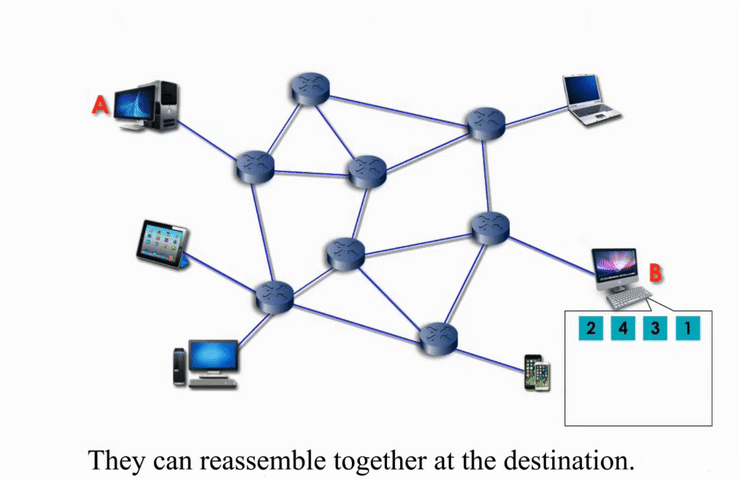
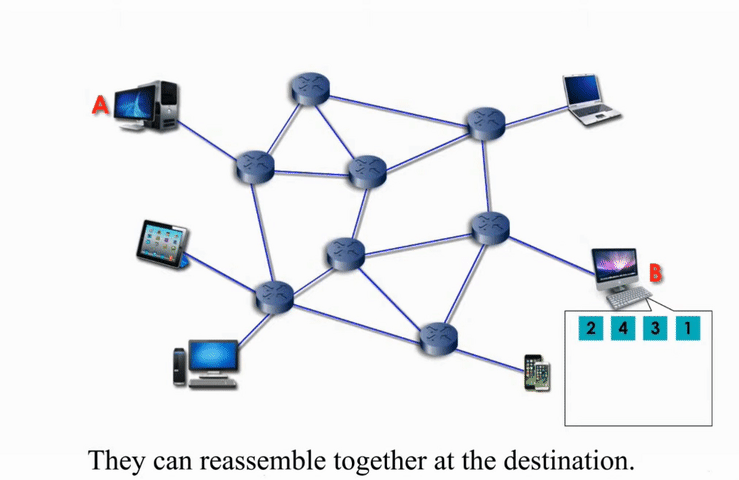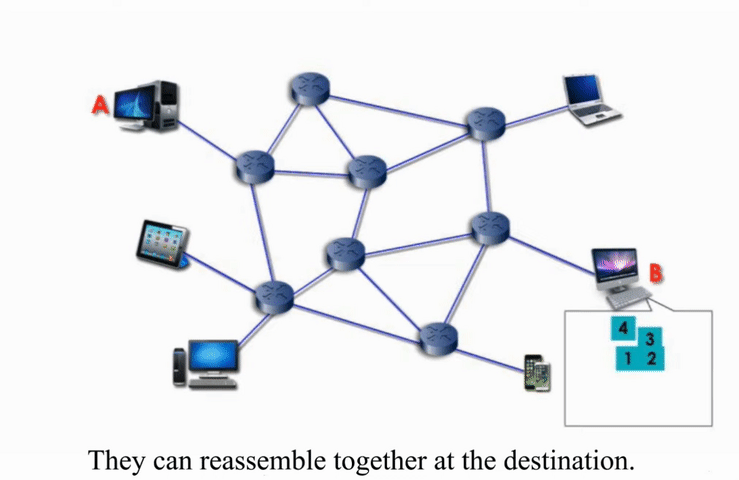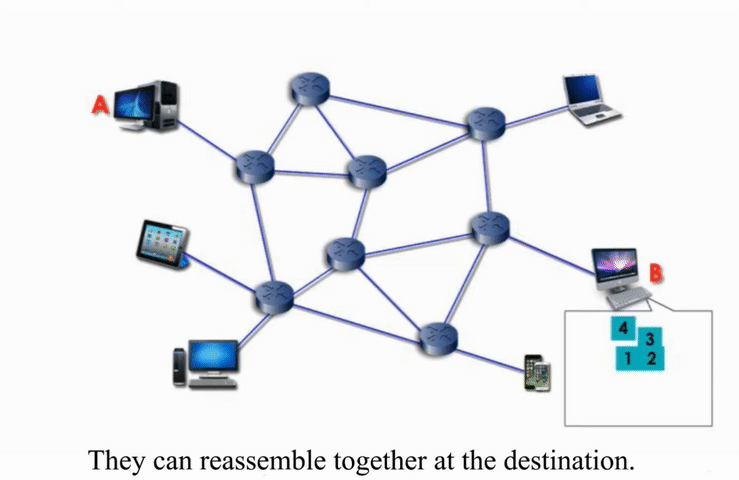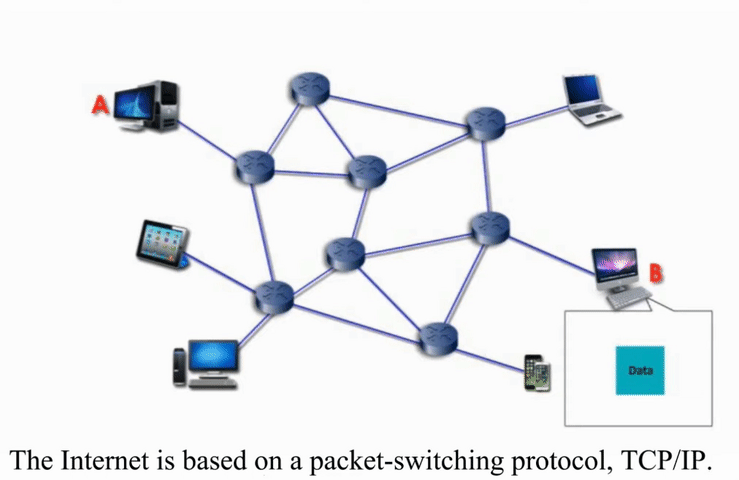
More flexible and more efficient if some amount of delay is acceptable
Normally handle digital data
Reference
Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching