Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
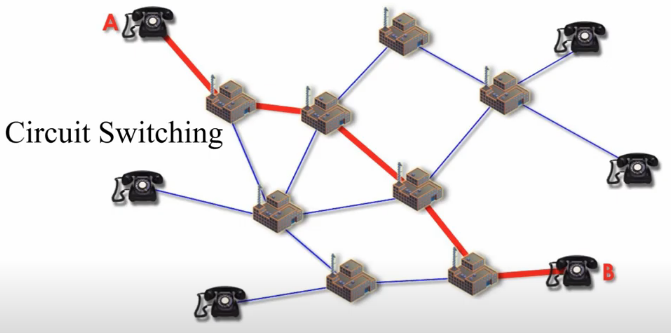
Recall: Packet Switching and Circuit Switching
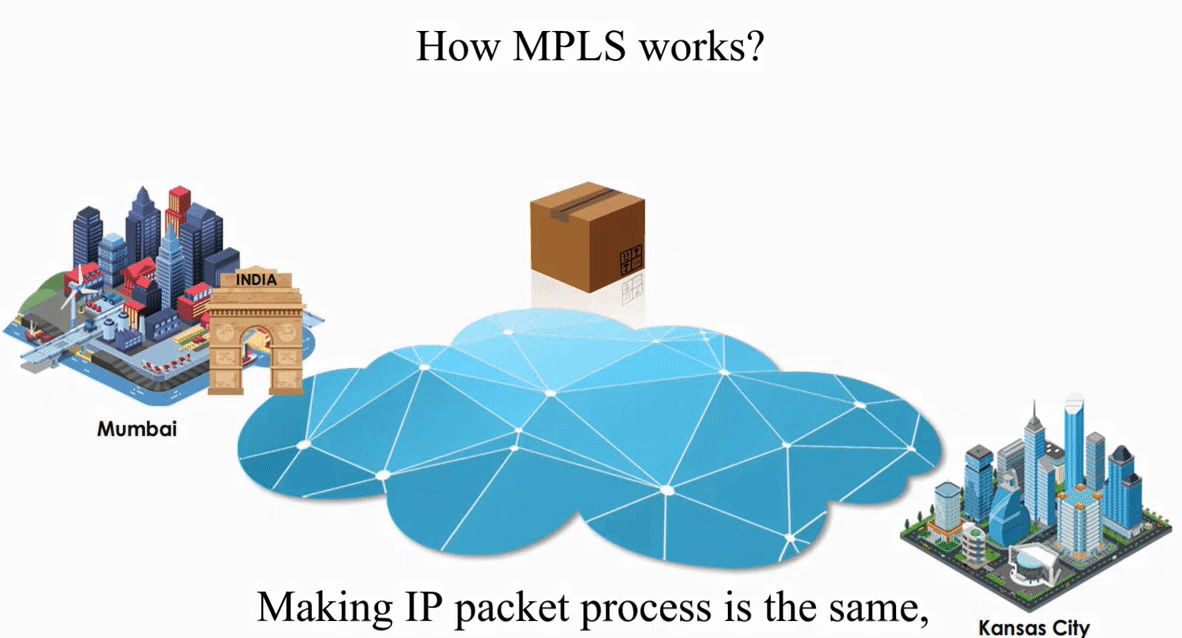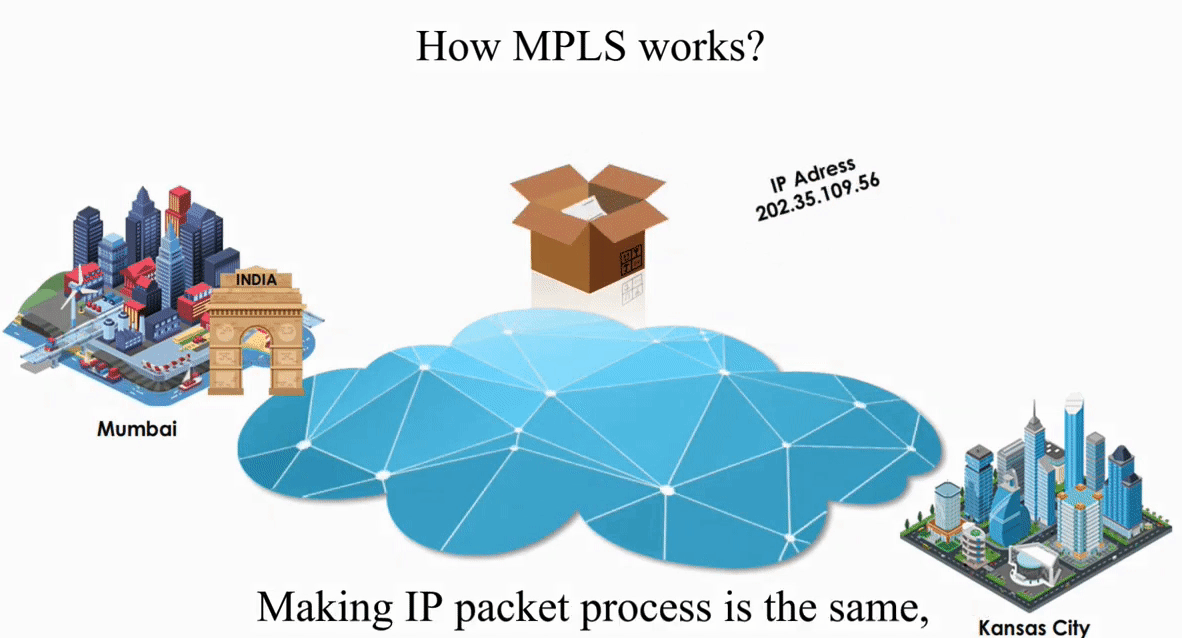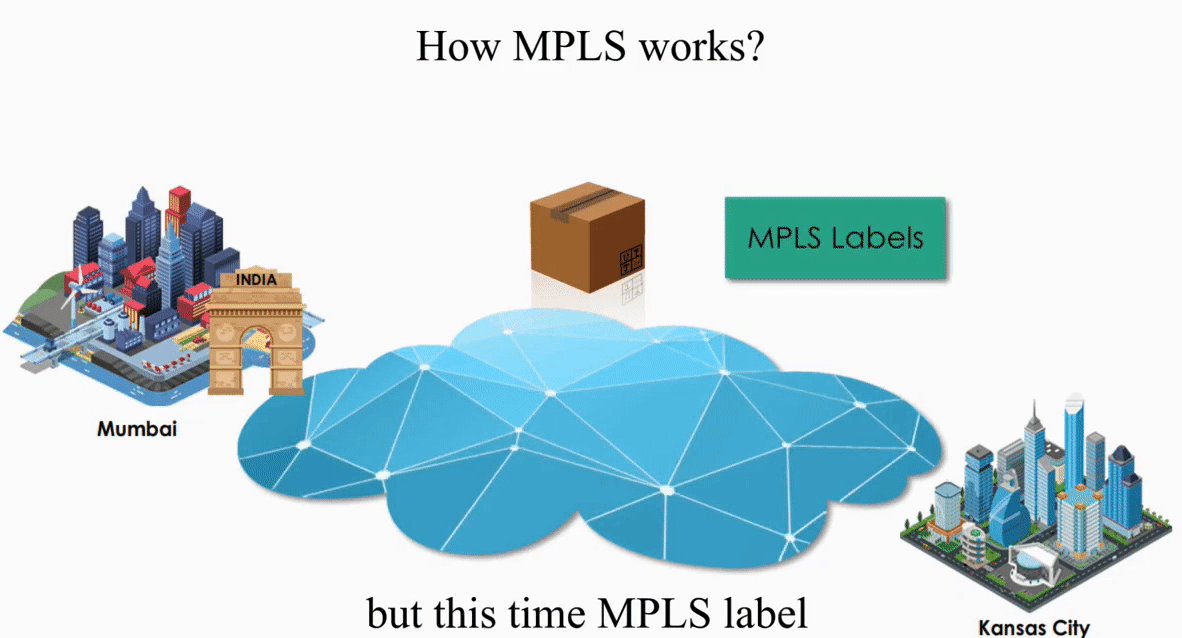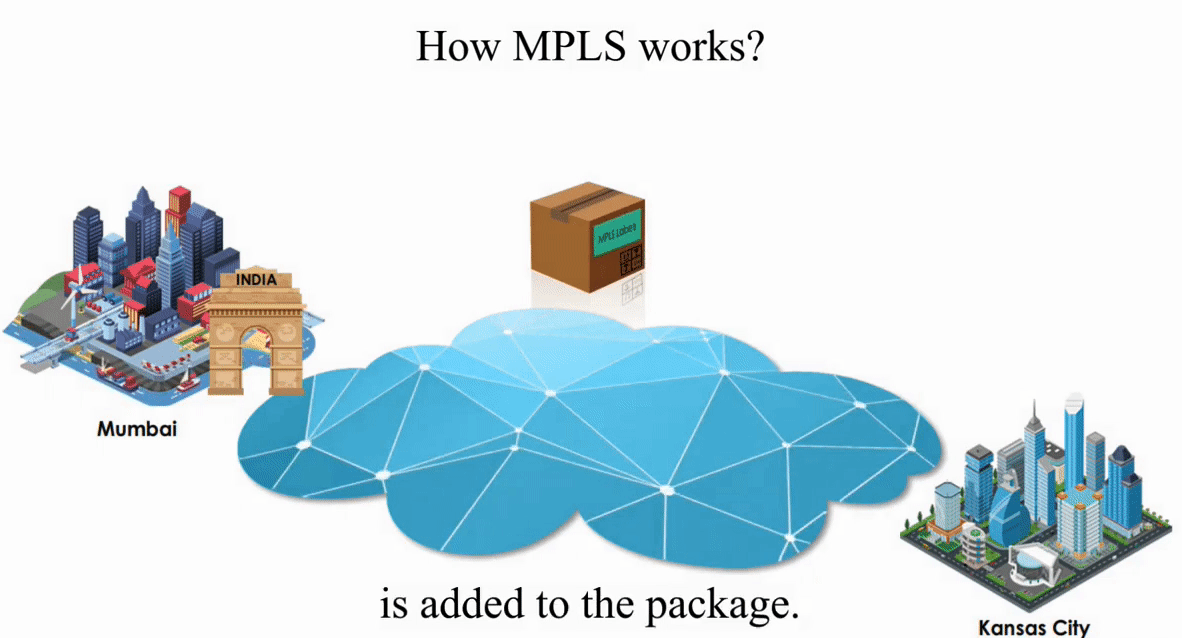
Suppose an IP packet is sent from Mumbai, India to Kansas City, Kansas using Packet switching
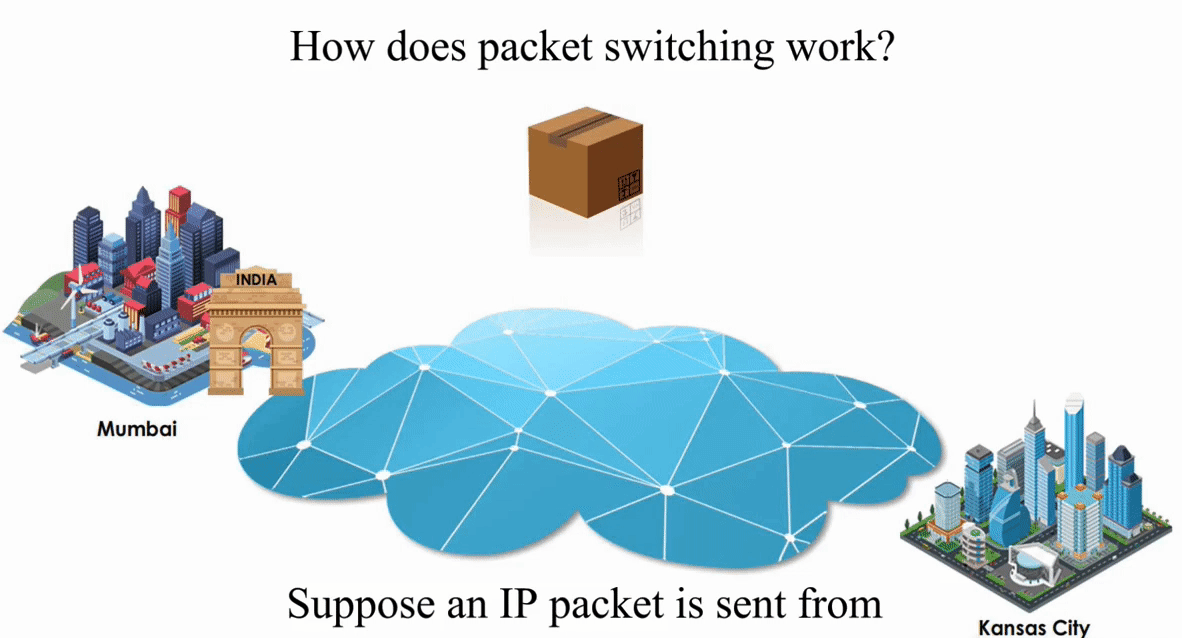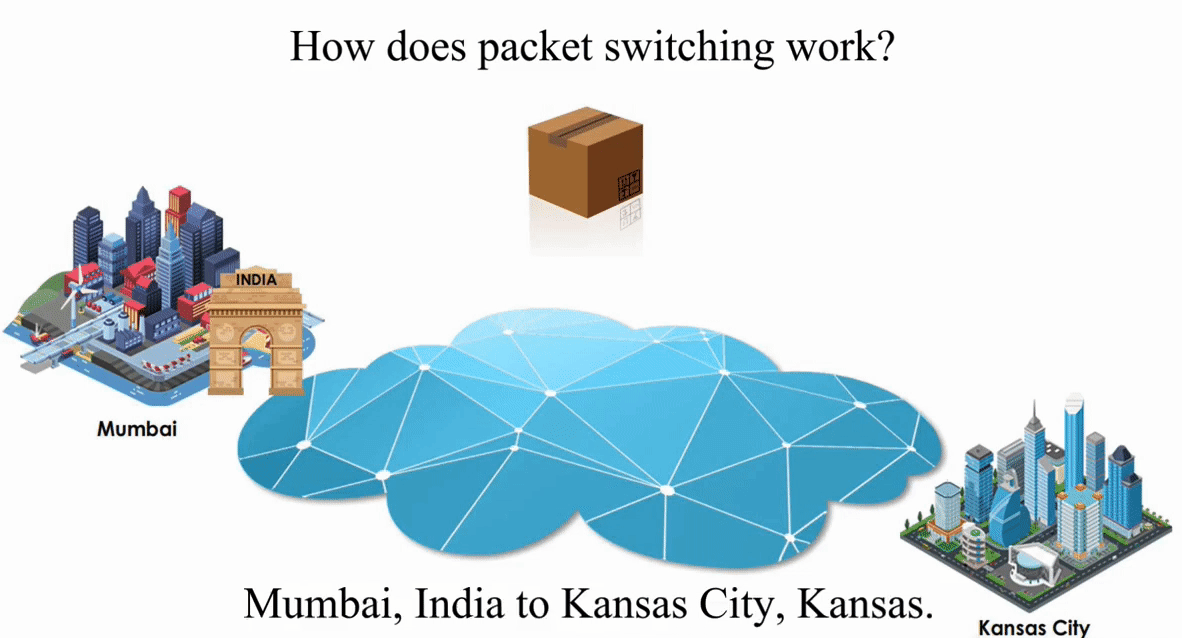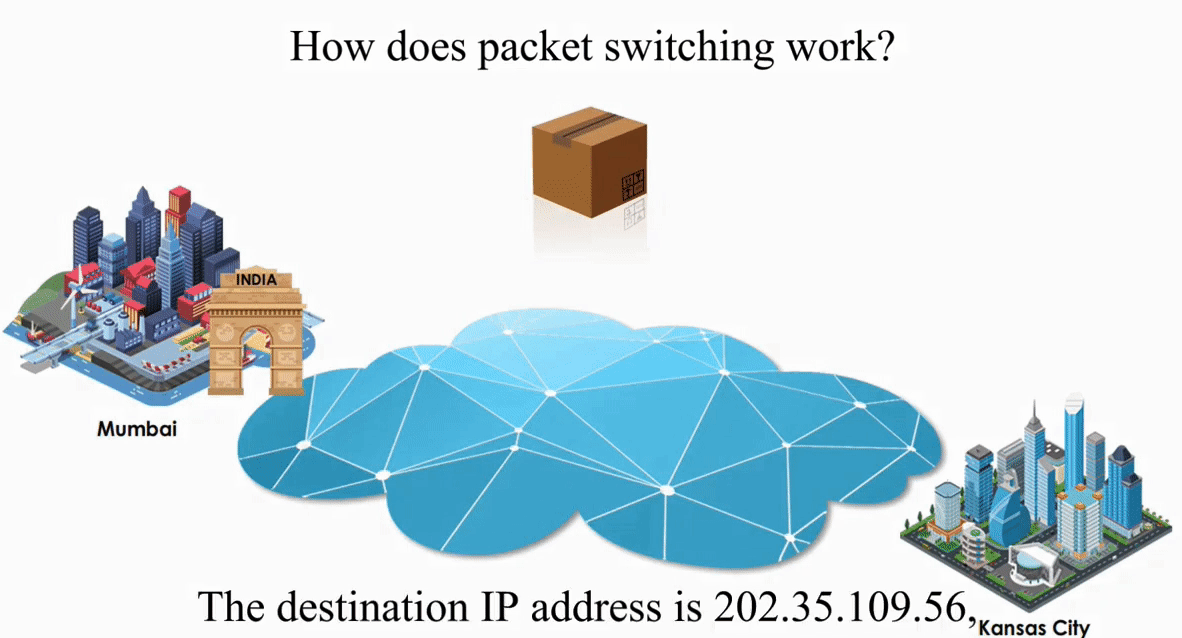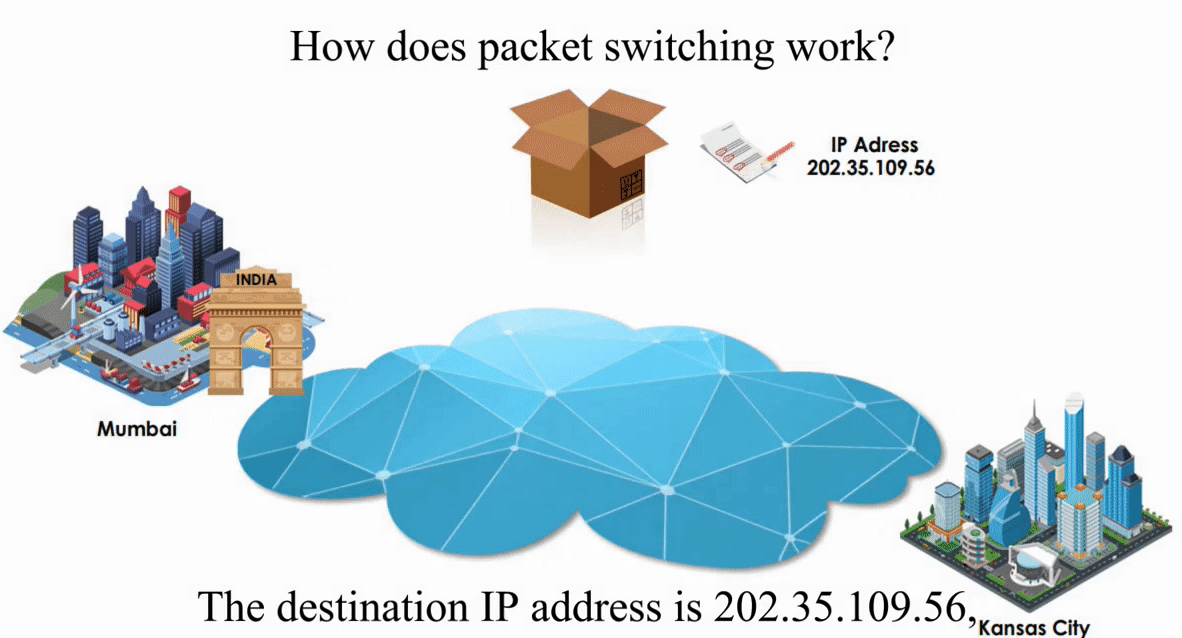
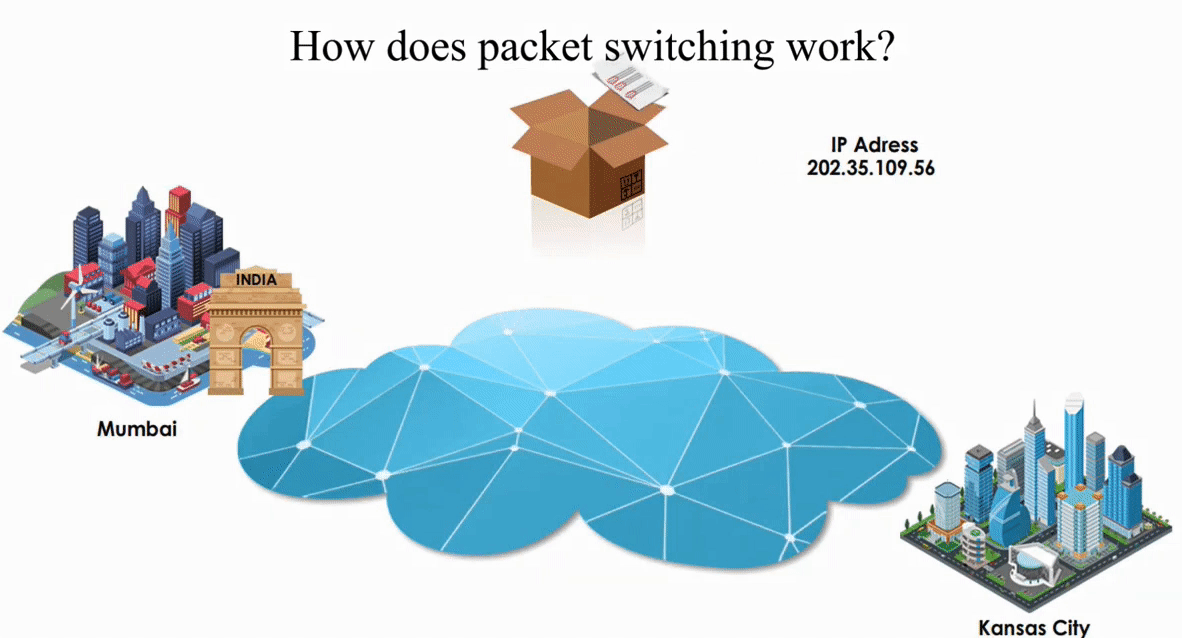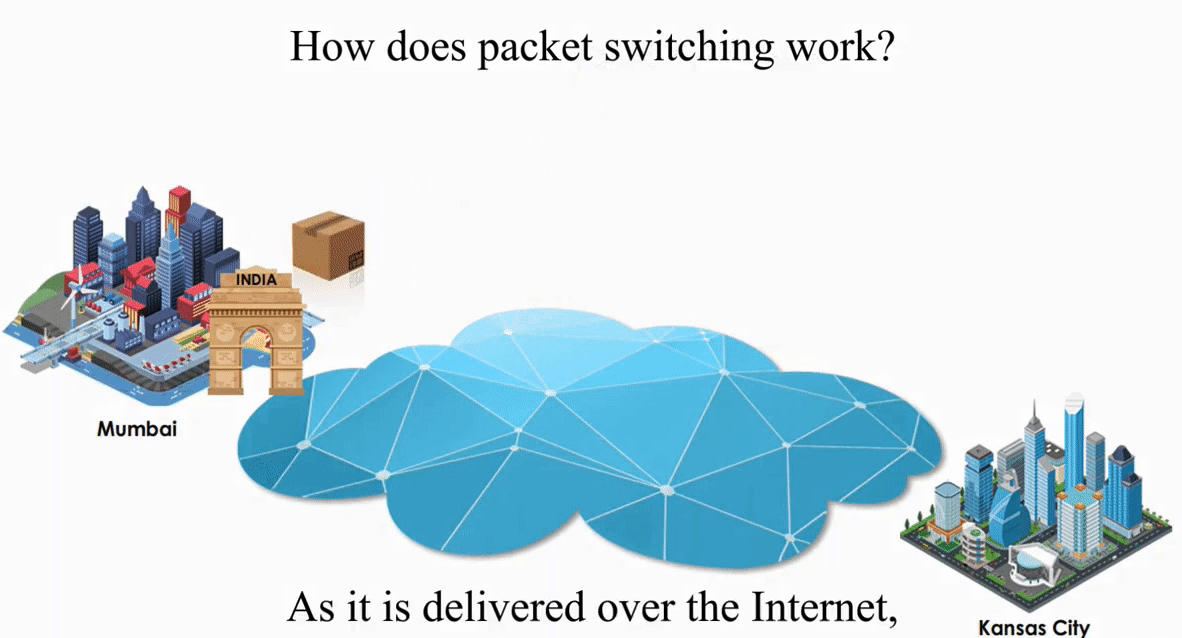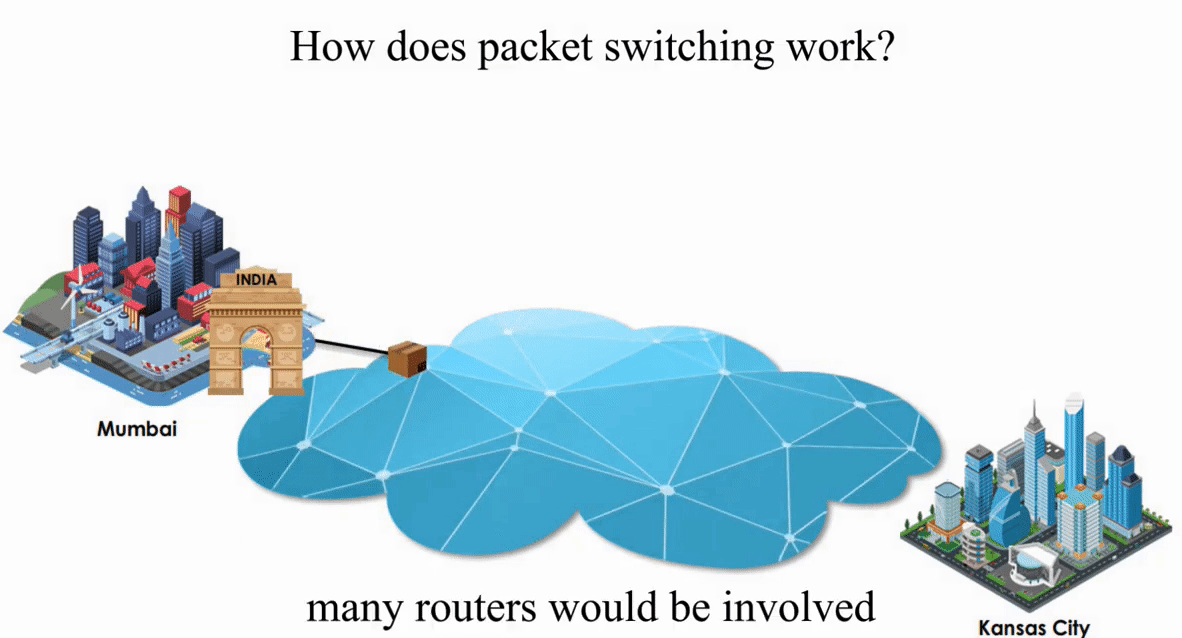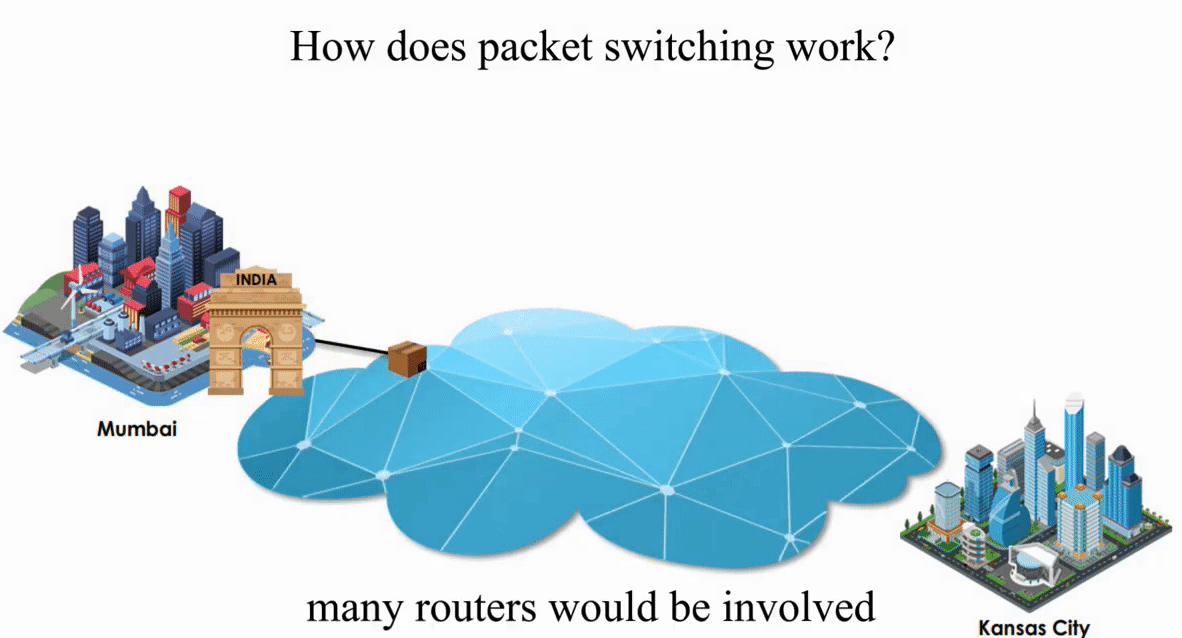
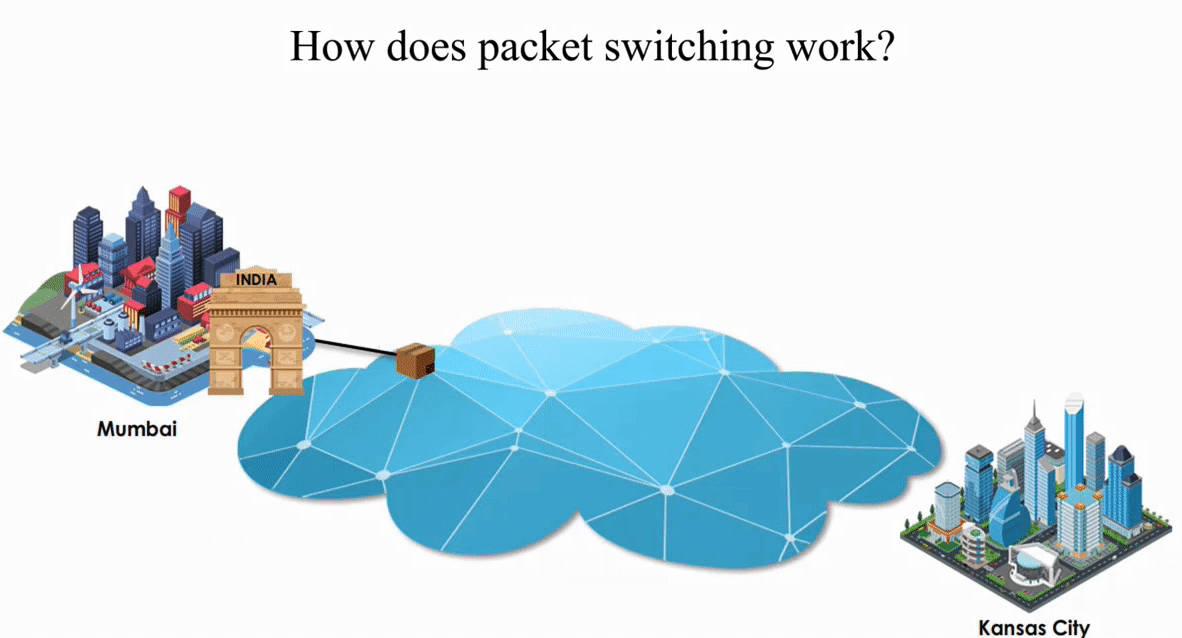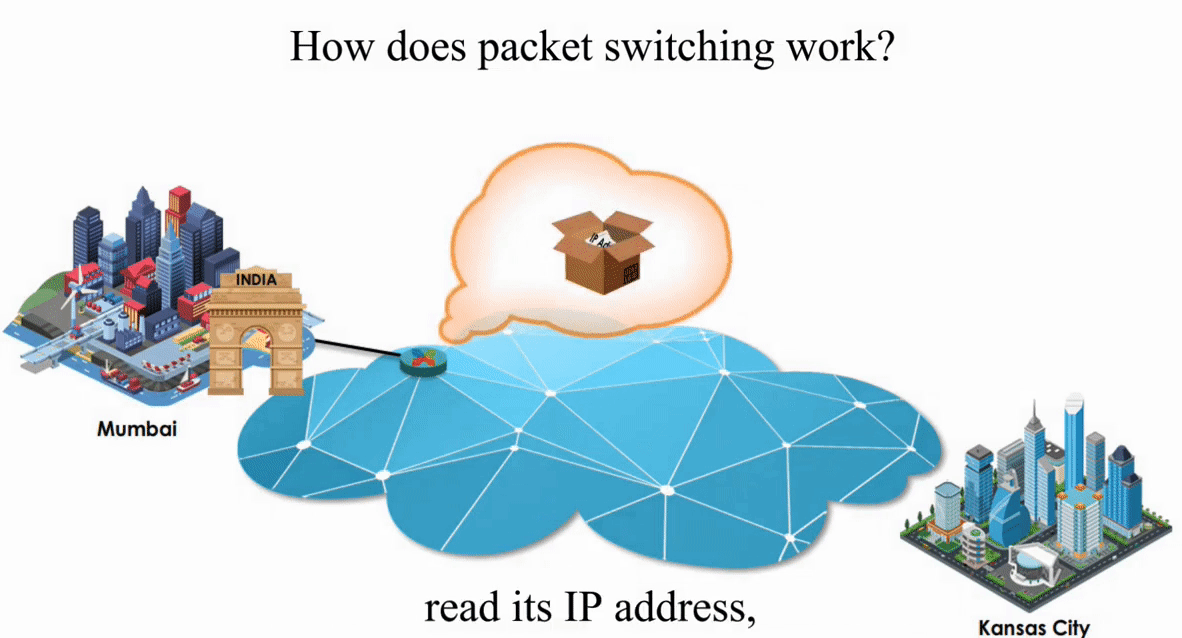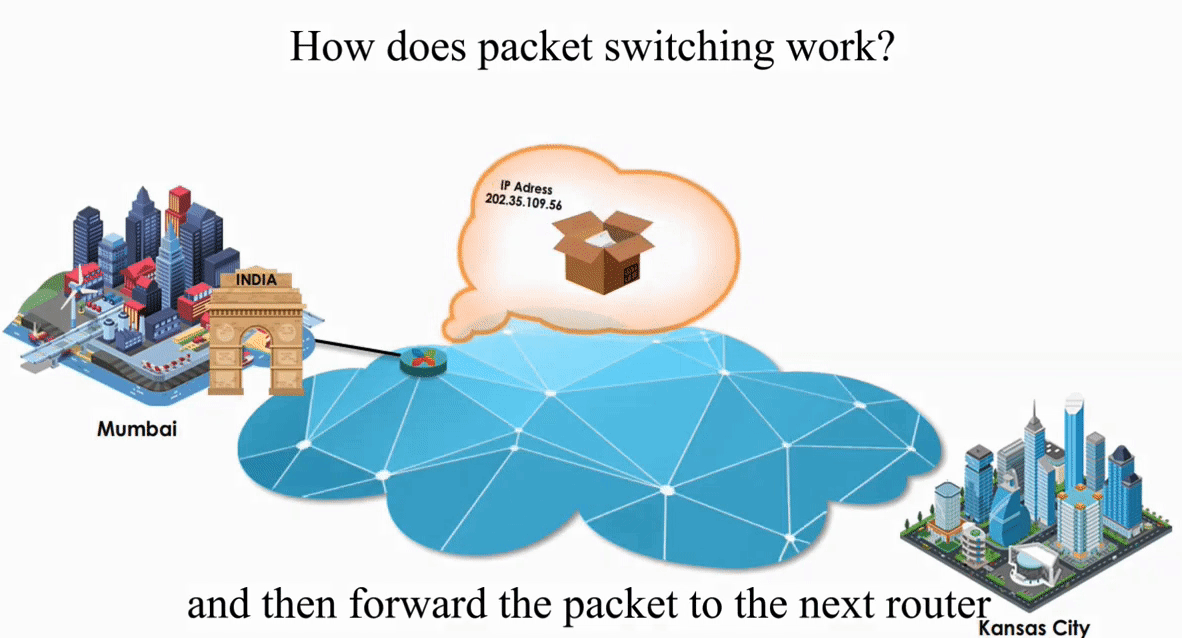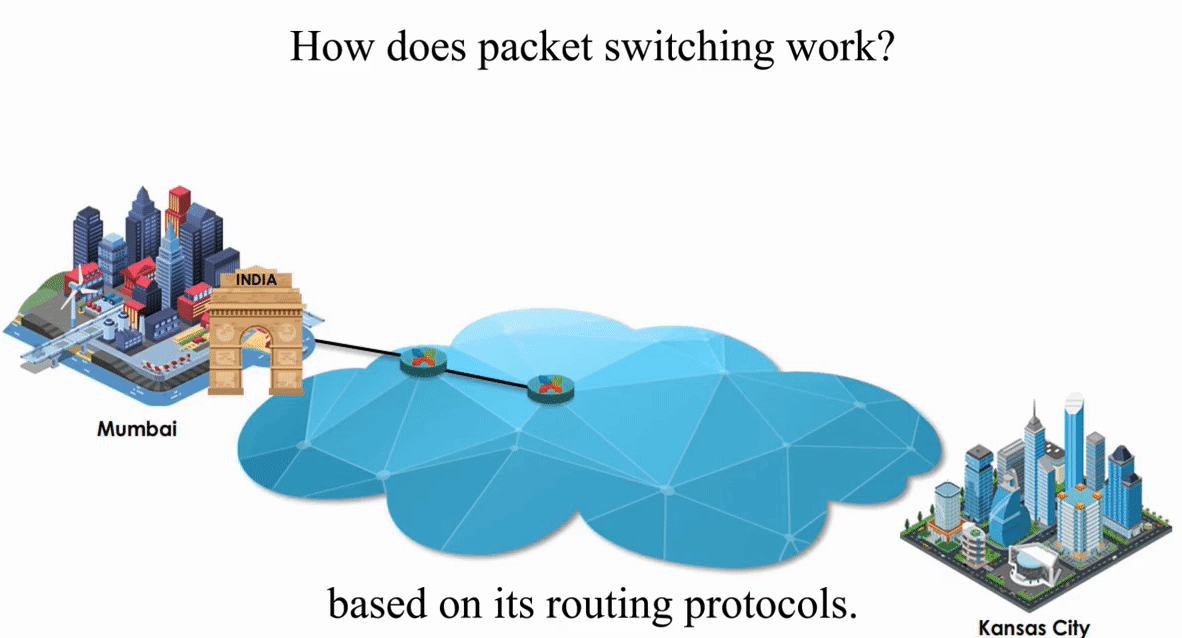
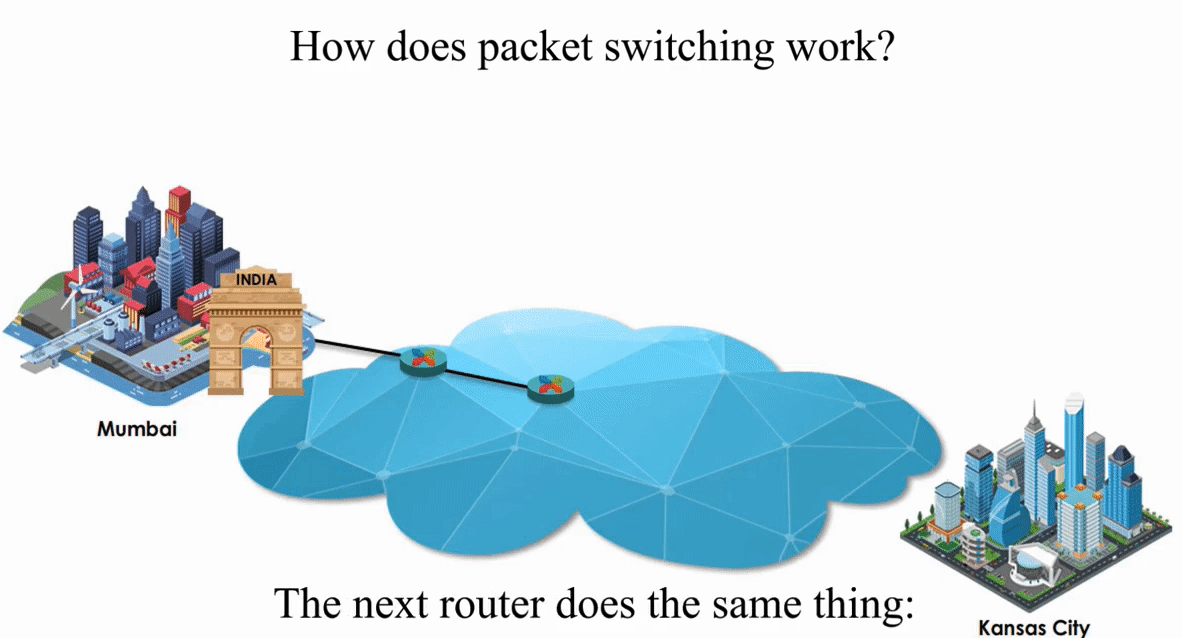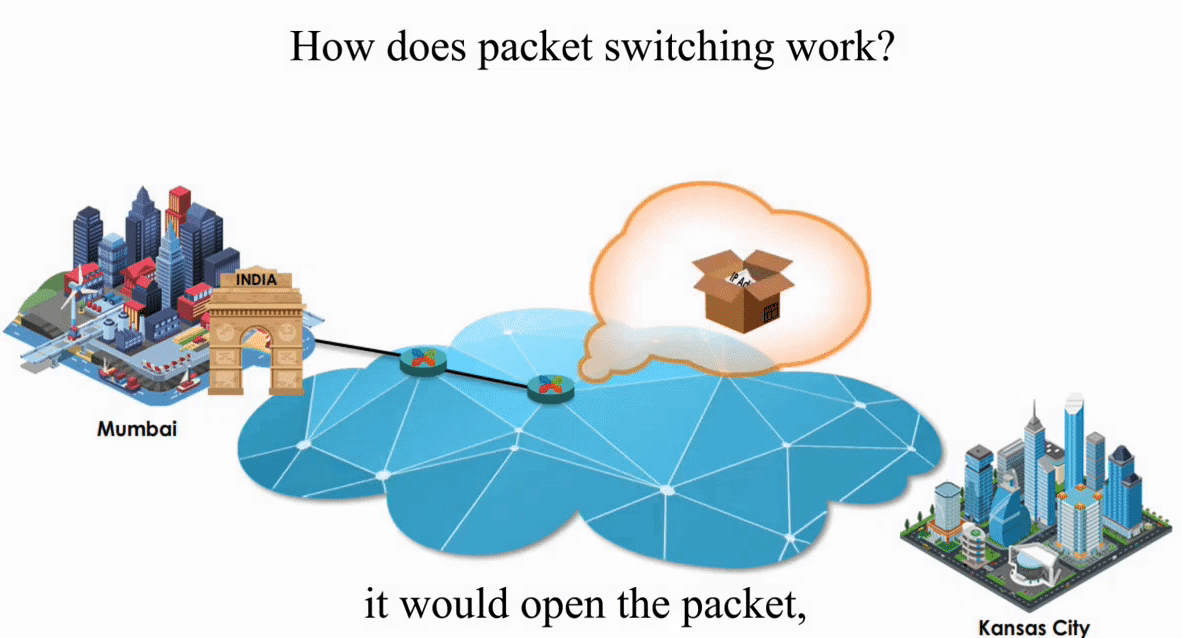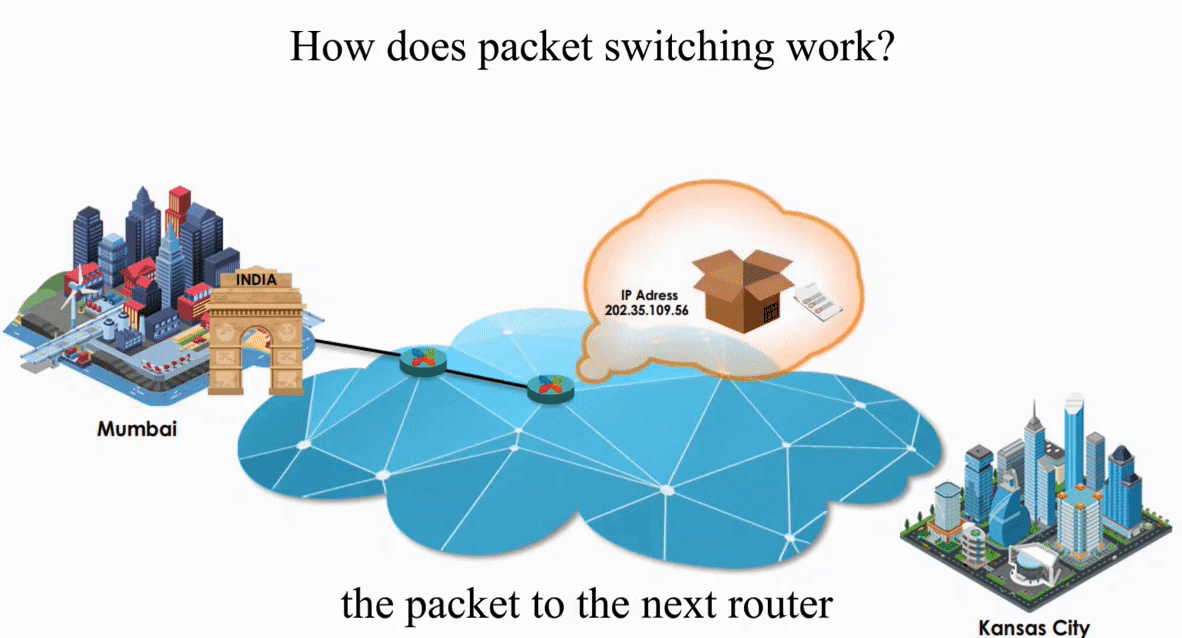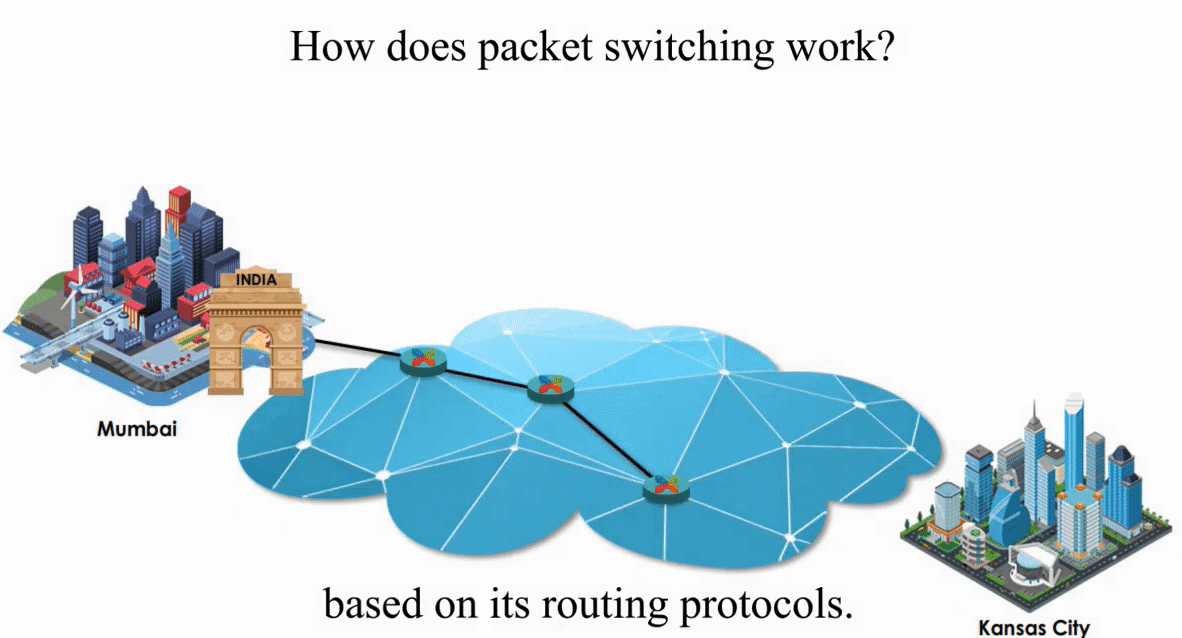
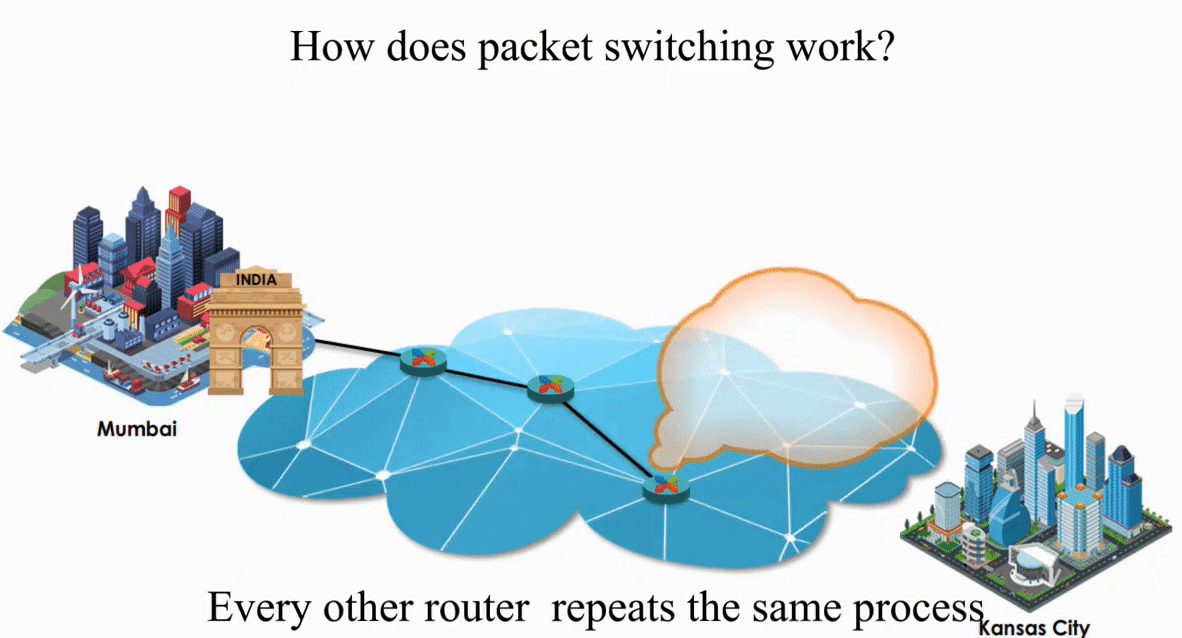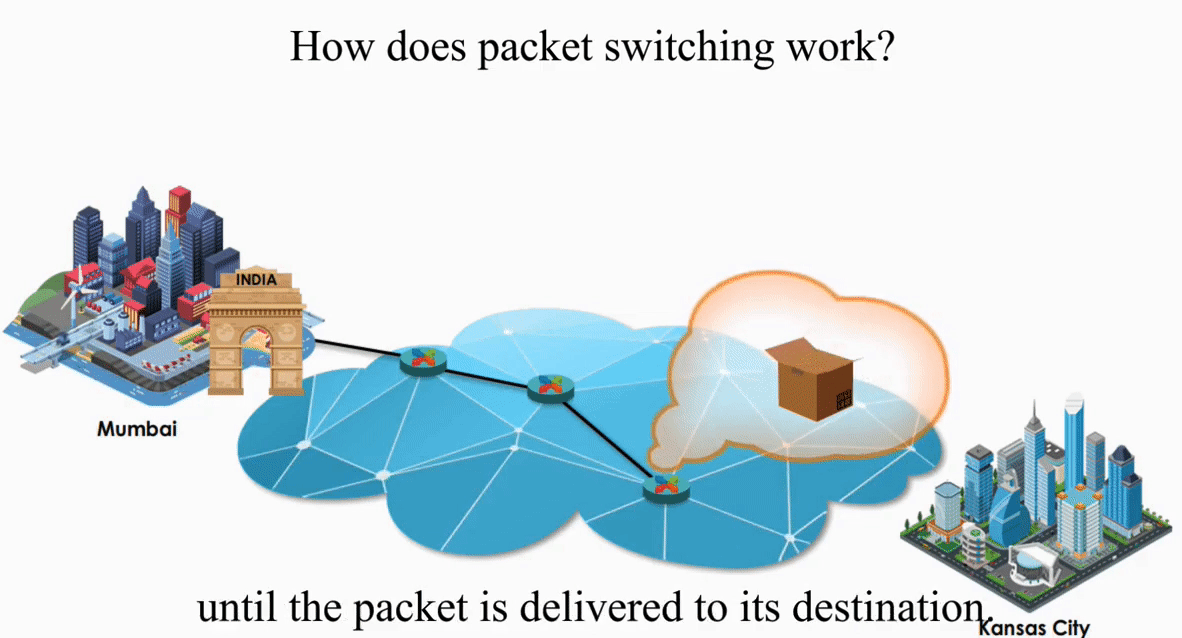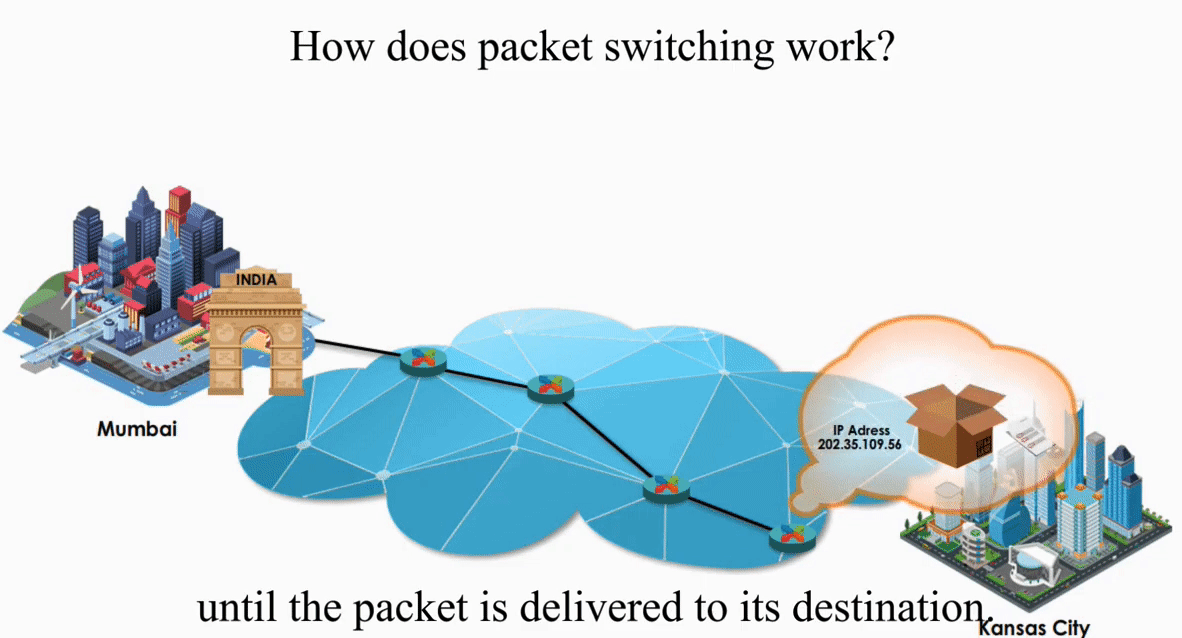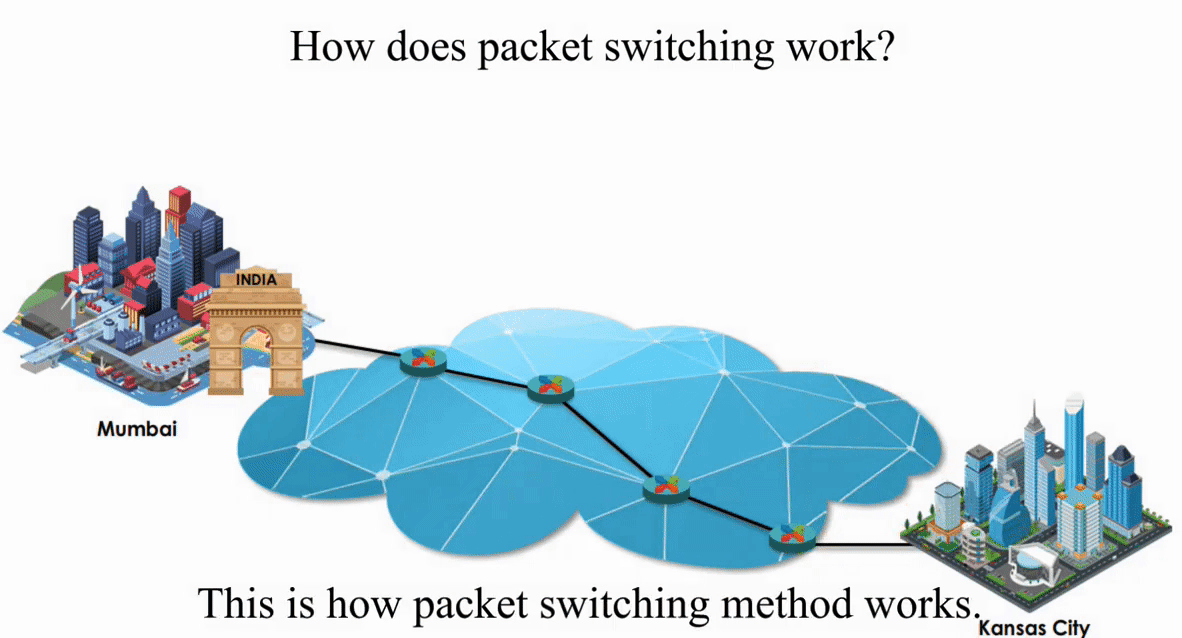
Packet switching is flexible and data path is not fixed. But processing IP information at every router slows down transmission.
In contrast, circuit switching method is a fixed-path switching method. It is reliable but more expensive.
MPLS
MPLS allows IP packets to be forwarded at layer 2 (switching level) without being passed up to layer 3 (routing level).
Let’s take a look how MPLS works with the same IP packet sent from Mumbai, India to Kansas City, Kansas.
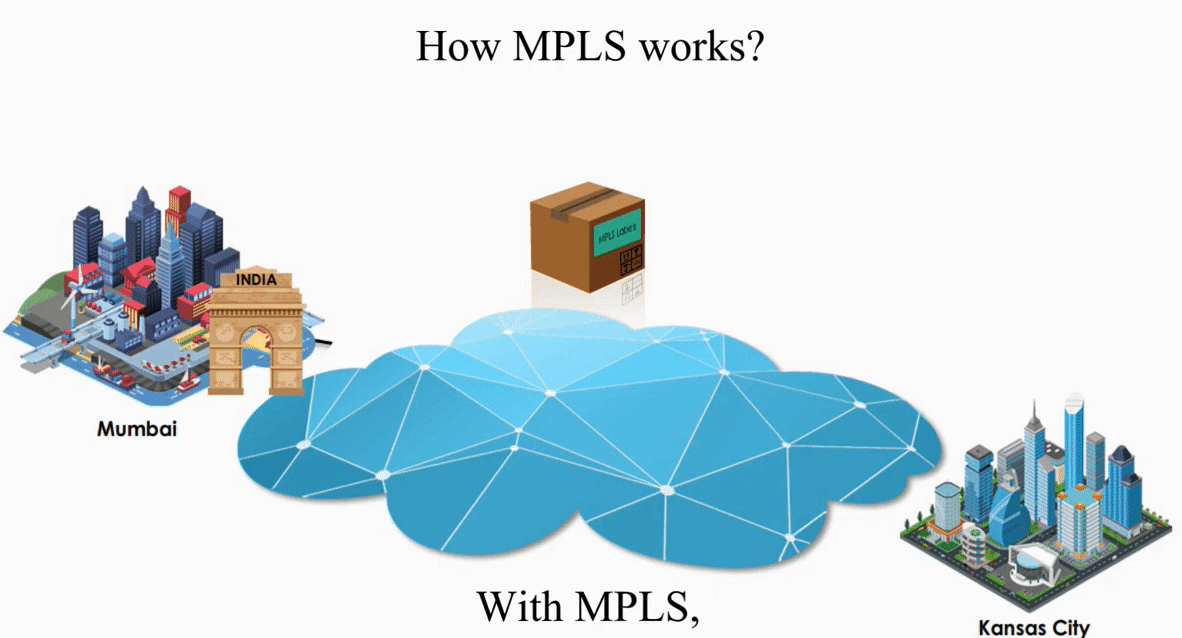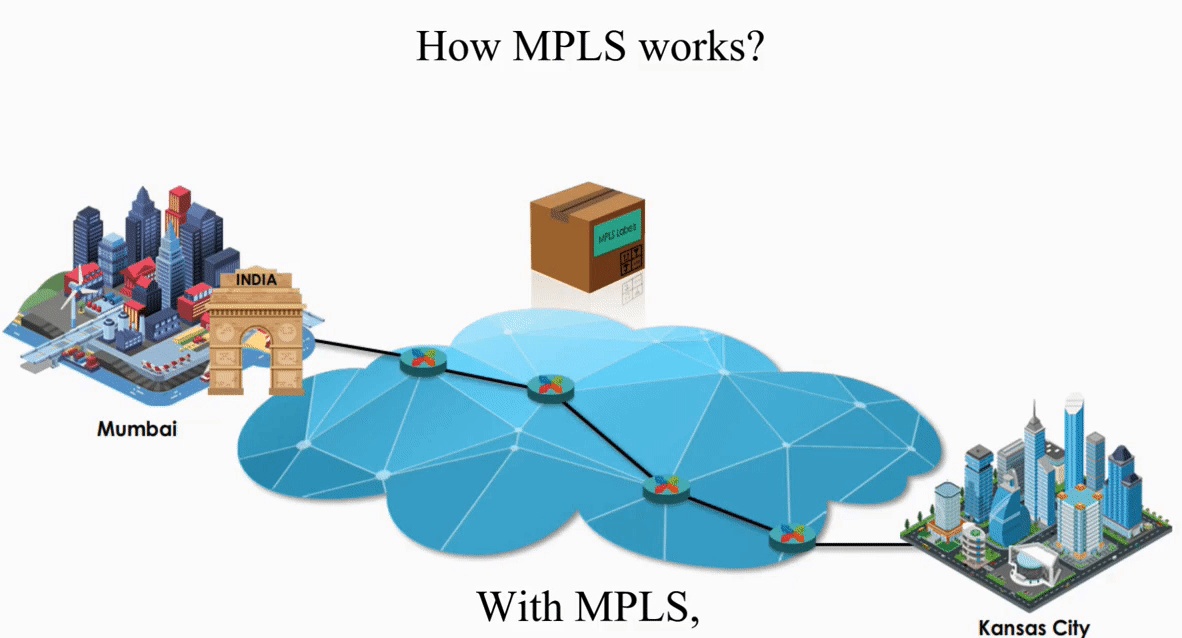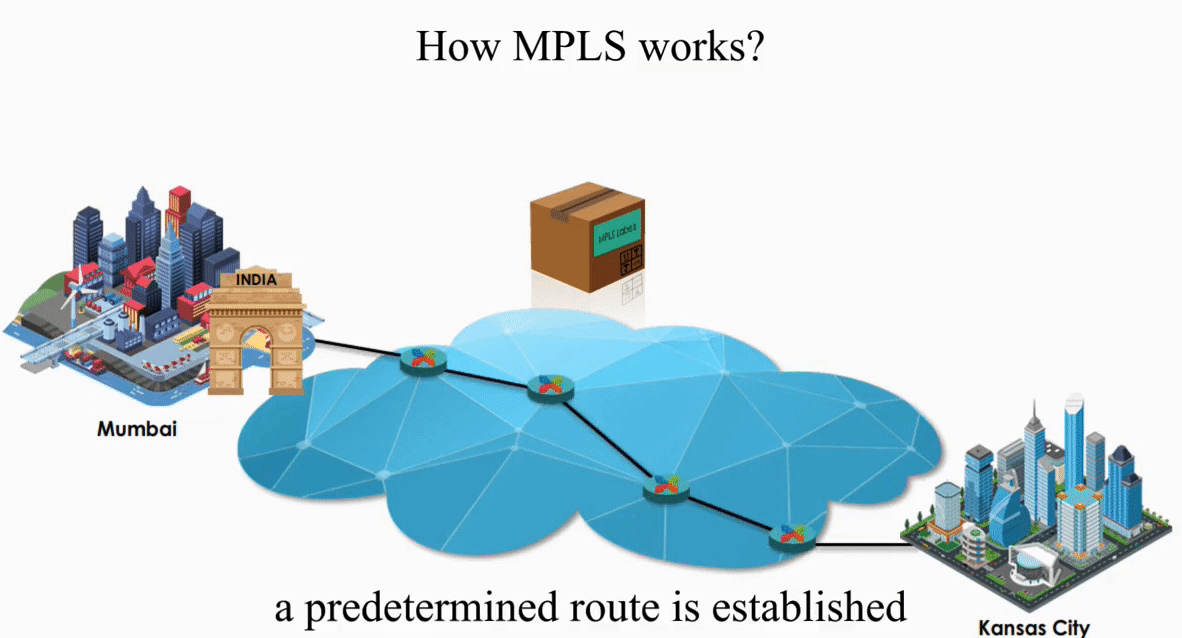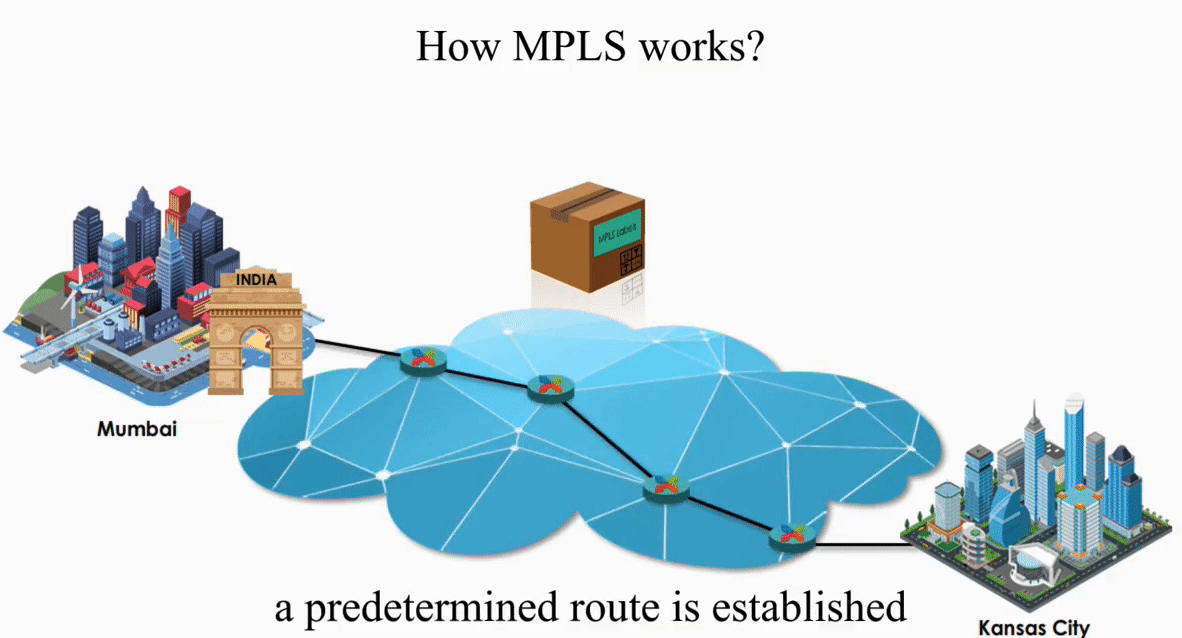
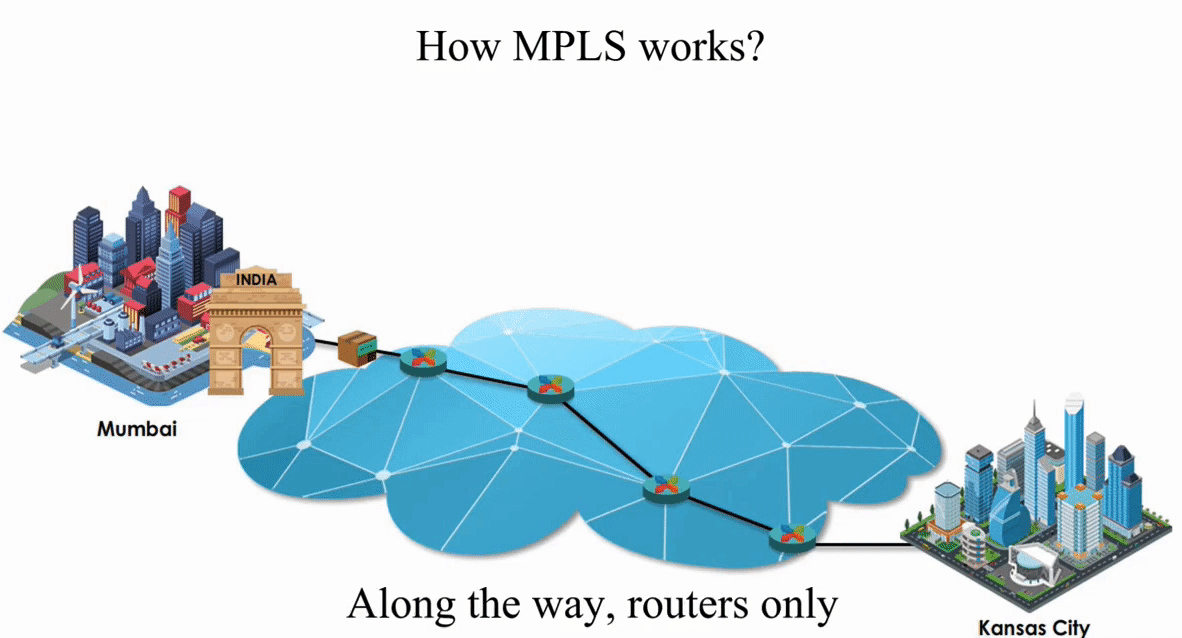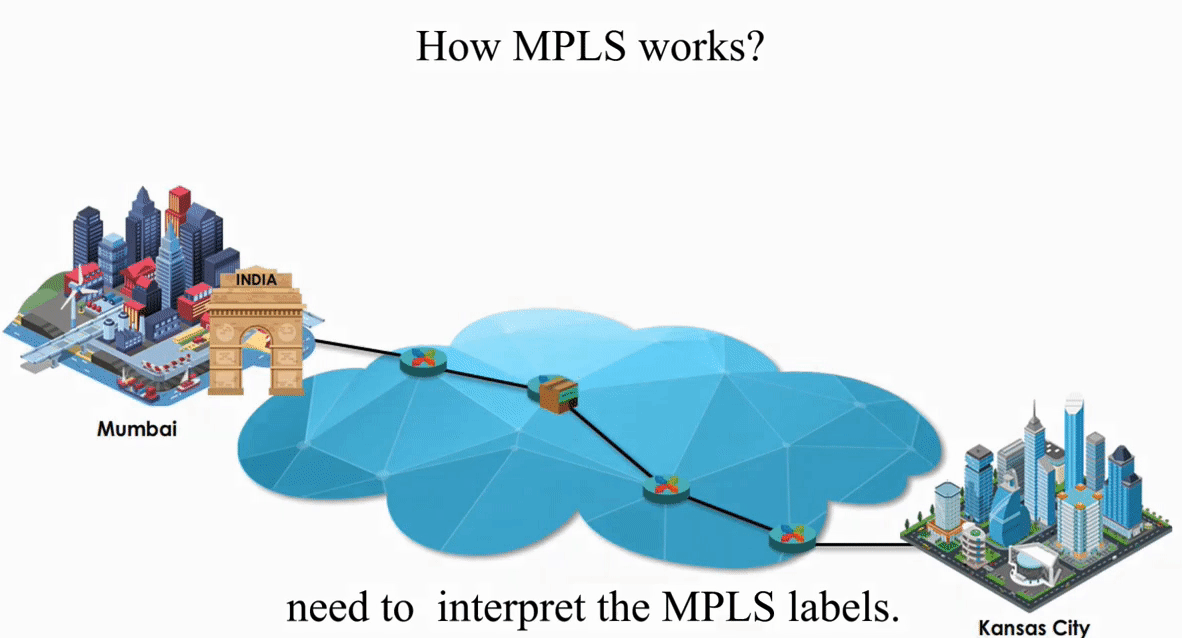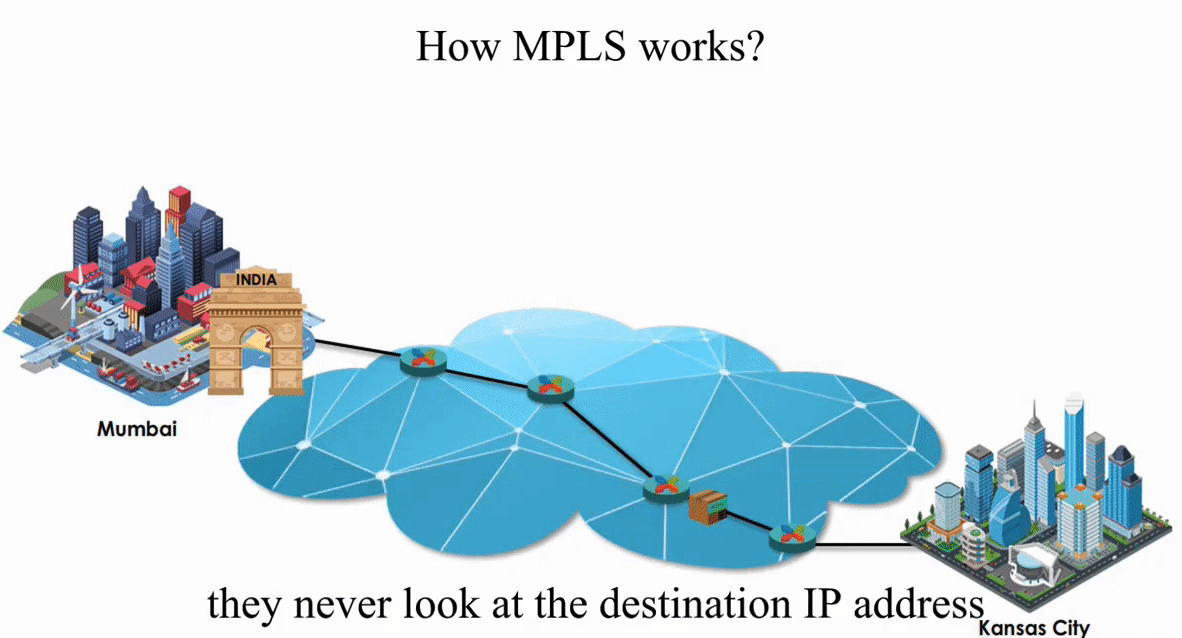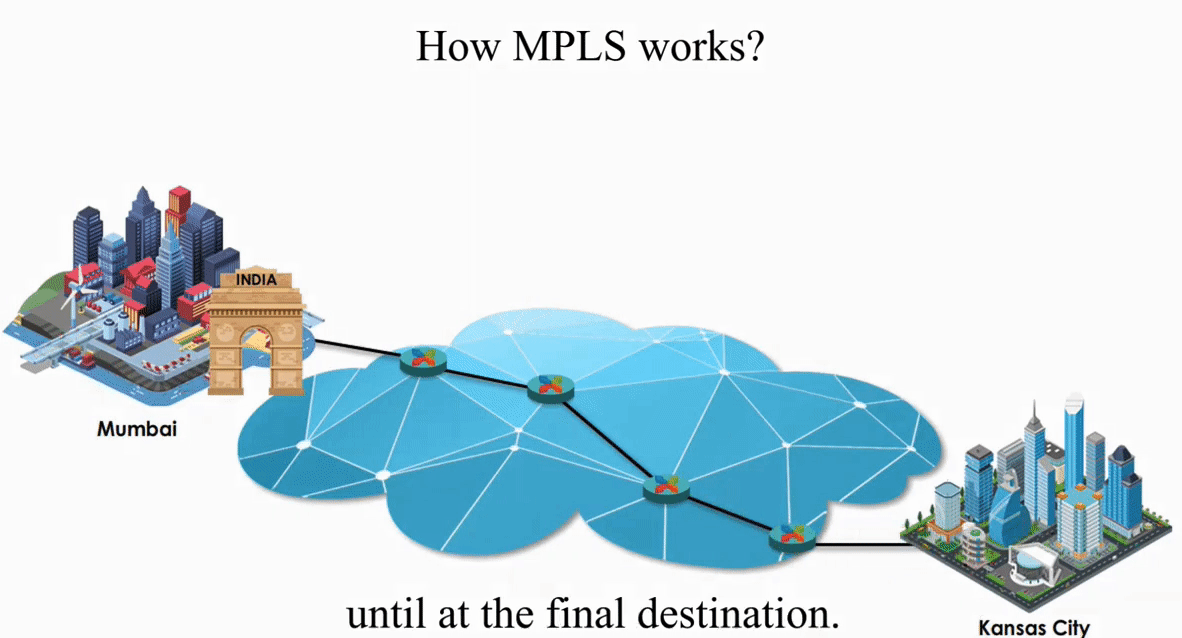
These routers act like switches on a local network.
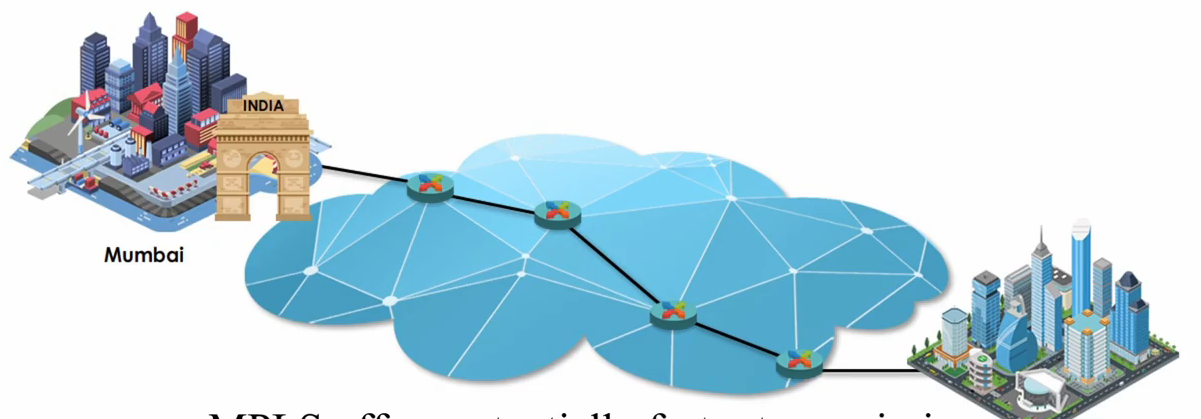
As a result, MPLS offers potentially faster transmission than traditionally packet switching networks 👏.
In summary, MPLS can create end-to-end paths that act like circuit-switched connections, but deliver layer 3 IP packet.
As we know, routing is the layer 3 function while switching is the layer 2 function. MPLS makes those routers on the Internet act like switches on a local network.
$\rightarrow$ MPLS is also called 2.5 layer protocol.
Reference
MPLS - Multiprotocol Label Switching (2.5 layer protocol)